FIGURE 1.
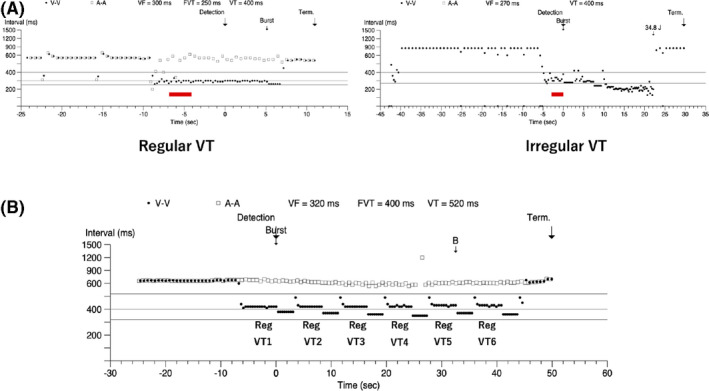
(A) Difference in the cycle length variability of VT. The left panel shows a constant cycle length, whereas the right panel shows the variation in the cycle length. (B) Example of multiple VT episodes within an episode. Regular VTs account for a larger number of VT types, classified by the variability within an episode. The RE value is calculated by dividing the number of regular VTs (6) to the number of total VTs in the episode (6). A‐A, atrial cycle length; RE, reproducibility in each episode; Reg, regular; Term, termination; VF, ventricular fibrillation; VT, ventricular tachycardia; V‐V, ventricular cycle length
