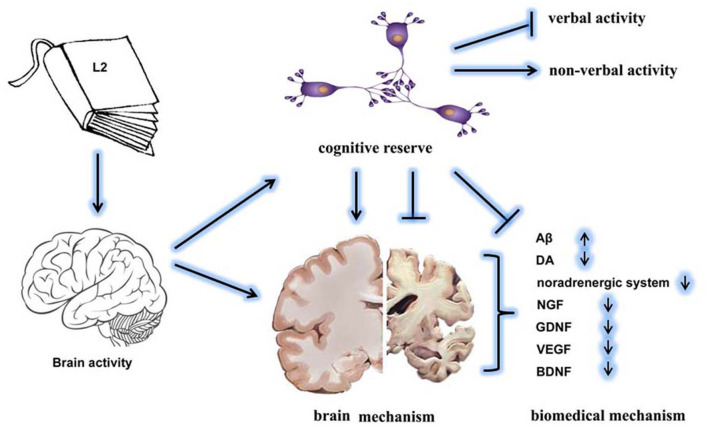
Figure 2.
The effects of bilingualism on delaying the onset of dementia. The L2 language exposure increases brain activity and cognitive reserve. Specifically, bilingualism increases non-verbal activity but decreases verbal activity. The underlying mechanisms might include brain mechanisms and biochemical mechanisms. Bilingualism-enhanced cognitive reserve effectively protects the brain structure and maintains the homeostasis of biochemical factors.