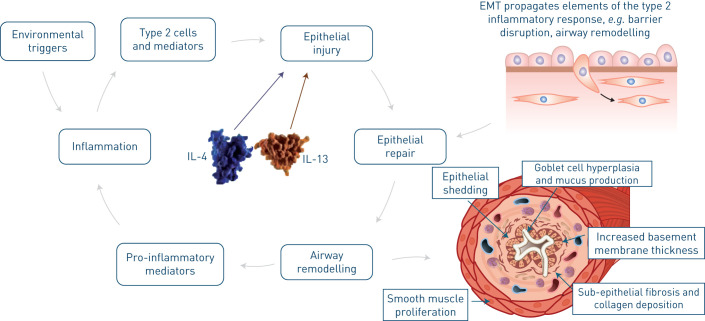
FIGURE 3.
Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 are central to airway remodelling. Environmental triggers begin the process of inflammation in the airway with stimulation of type 2 inflammatory cells and mediators, including IL-4 and IL-13, which damage the epithelium. Repair is propagated from the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), leading to barrier disruption and remodelling of the airway. This remodelling results in epithelial shedding, increased thickness of the basement membrane, fibrosis and collagen deposition, smooth muscle proliferation, goblet cell hyperplasia and mucus production. Additionally, remodelling results in increased pro-inflammatory mediators, which further increase inflammation and epithelial damage.