Figure 4.
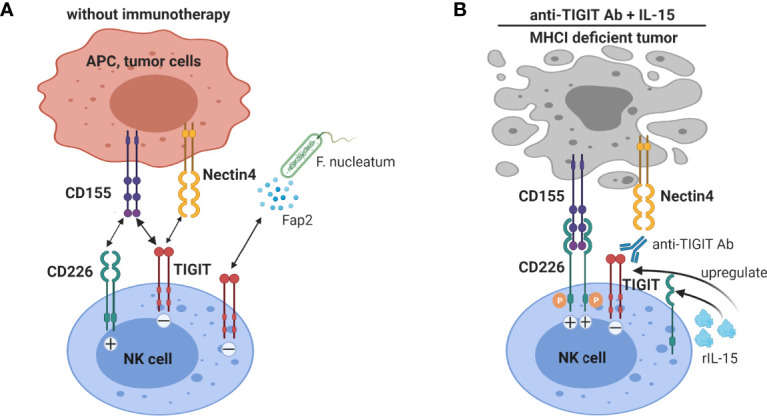
Blockade of TIGIT on NK cells augments anti-tumor immunity. (A) NK cells expressing TIGIT are functionally impaired by binding to CD155 and nectin-4, and in colorectal cancer to Fap2 protein produced by a gut bacterium. (B) TIGIT blockade not only interrupts inhibitory signaling by TIGIT in NK cells, but also allows interaction of the co-stimulatory receptor CD226 with CD155. IL-15 treatment increases TIGIT and CD226 expression on NK cells. Thus IL-15 combined with TIGIT blockade further enhanced NK cells anti-tumor functions, especially promoting NK cell-mediated destruction of MHC class I-deficient tumors.
