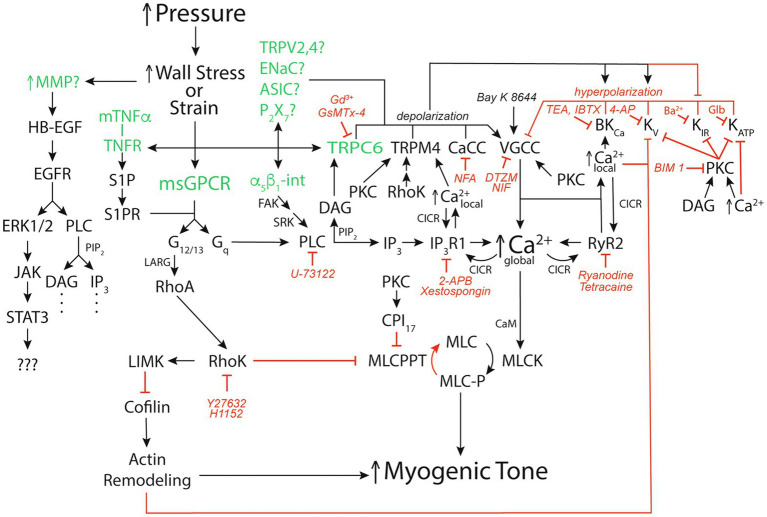
Figure 2.
Signaling pathways for pressure-induced myogenic tone. Schematic diagram of reported signaling pathways involved in myogenic tone in resistance arteries and arterioles. Green font color depicts putative mechanosensors in pressure-induced myogenic tone. Black arrows show stimulation, increases or activation of signaling molecules, ion channels, or enzymes that participate in myogenic tone. Red capped lines indicate inhibition, decreases or deactivation of signaling molecules, ion channels, or enzymes involved in myogenic tone. Also shown are pharmacological agents that we have used to interrogate the ion channels and signaling pathways in arteriolar myogenic tone. MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; HB-EGF, heparin-bound epidermal growth factor; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK1/2, extracellular-signal-related kinases 1 or 2; JAK, janus kinase; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; mTNFα, membrane-bound tumor necrosis factor α; TNFR, TNFα Receptor; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; S1PR, S1P receptor; α5β1-int, α5β1 integrin: FAK, focal adhesion kinase; SRK, Src-related kinases; CaCC, Ca2+-activated Cl− channel; TRPV2,4, transient receptor potential vanilloid-family 2 or 4 channels; ENaC, epithelial Na+ channel; ASIC, acid sensing ion channel; P2X7, P2X7 purinergic receptor; VGCC, voltage-gated Ca2+ channel; BKCa, large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel; KV, voltage-gated K+ channel; KIR, inwardly-rectifying K+ channel; KATP, ATP-sensitive K+ channel; msGPCR, mechanosensitive G-protein-coupled receptor; DAG, diacylglycerol; PKC, protein kinase C; NFA, niflumic acid; DTZM, diltiazem; NIF, nifedipine; TEA, tetraethylammonium; IBTX, iberiotoxin; 4-AP, 4-aminopyridine; GLIB, glibenclamide; BIM I, bisindolylmaleimide I; PLC, phospholipase C; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate; IP3, inositol, 1,4,5 trisphosphate; IP3R1, IP3 receptor 1; RyR, ryanodine receptor; CICR, Ca2+-induced-Ca2+ release; LARG, guanine nucleotide exchange factor LARG; RhoA, small G-protein Rho; 2-APB, 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate; RhoK. Rho kinase; LIMK, LIM kinase; CPI17, C-kinase potentiated protein phosphatase-1 Inhibitor; MLCPPT, myosin light-chain phosphatase; MCL, myosin light-chain; MLCK, myosin light-chain kinase; See text for more details and references.