Figure 2. LSD1‐containing small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) fuse to the recipient cell and deliver LSD1.
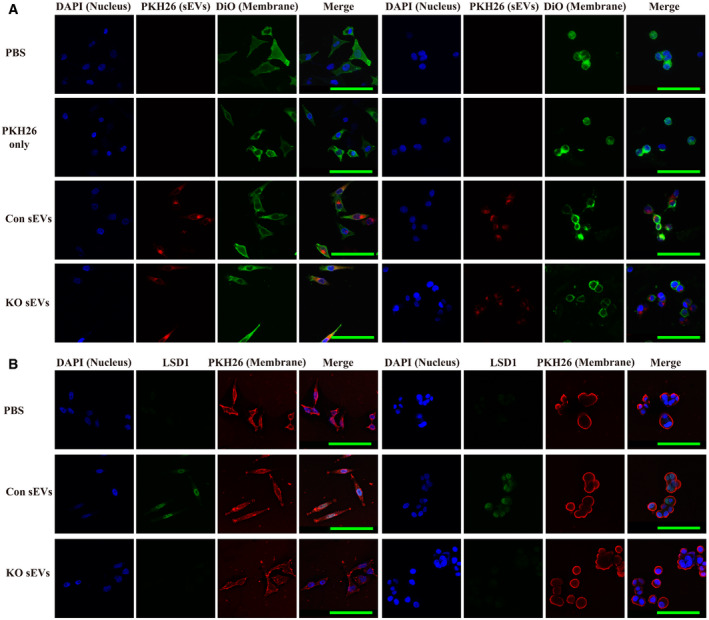
- Confocal microscopy image analysis of sEV fusion to MGC‐803 cells. The MGC‐803 (left side) and MKN‐45 (right side) cells were treated with sEVs derived from MGC‐803 cells (Con sEVs) or LSD1 knockout (KO) MGC‐803 cells (KO sEVs) and stained with PKH26 for 12 h. Additionally, the cell membrane was stained with Dio, while the nuclei were stained with 4',6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (DAPI). Scale bar = 100 µm.
- Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy analysis of LSD1 (green) in LSD1 KO MGC‐803 cells (left panel) and LSD1 KO MKN‐45 cells (right panel) incubated with 20 μg/ml Con sEVs and KO sEVs for 12 h. The cell membrane was stained with PKH26, while the nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bar = 100 µm.
