-
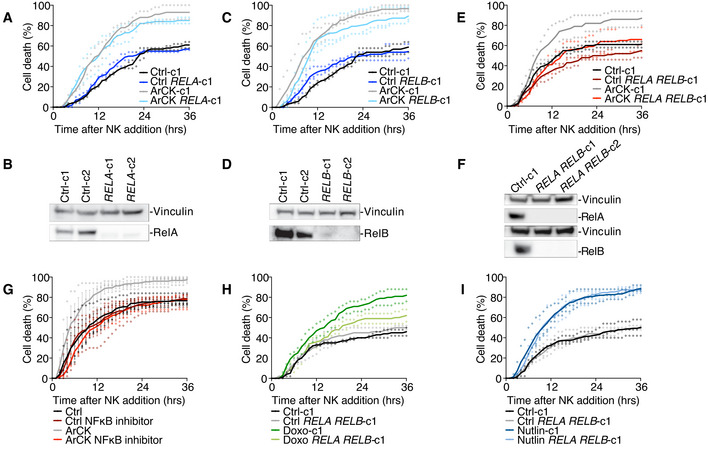
A
NK cell‐mediated killing of RELA ArCK cells was compared with clones harboring an empty vector. ArCK RELA knockout cells were generated, and the NK cell‐mediated cytotoxicity was measured as described in the Method section. Dot plot of individual data points and mean was presented. n = 2 biological replicates; ArCK‐c1 vs. ArCK RELA‐c1, P = 0.70, n.s.; KS test.
-
B
Measurement of RelA protein levels in RELA KO single cell clones generated in RPE1‐hTERT cells.
-
C
The effect of inactivating RELB on NK cell‐mediated cytotoxicity in ArCK cells. The same experimental methods were used as described in (A). n = 3 biological replicates; ArCK‐c1 vs. ArCK RELB‐c1, P = 0.47, n.s.; KS test.
-
D
Measurement of RelB protein levels in RELB KO single cell clones generated in RPE1‐hTERT cells.
-
E
The effect of inactivating both RELA and RELB on NK cell‐mediated cytotoxicity in ArCK cells. n = 2 biological replicates; ArCK‐c1 vs. ArCK RELA RELB‐ c1, P = 0.0014; KS test.
-
F
Measurement of RelA and RelB protein levels in RELA RELB double KO single cell clones generated in RPE1‐hTERT cells.
-
G
ArCK or euploid proliferating control cells were treated with either DMSO or the NF‐κB inhibitor BMS‐345541 (5 μM) for 48 h before assessing NK cell‐mediated cytotoxicity. The drug was washed out during the NK cell co‐culture assay. n = 3 biological replicates; mean ± SEM. ArCK vs. ArCK NF‐κB inhibitor, P < 0.0001; KS test.
-
H, I
The effect of inactivating both RELA and RELB on NK cell‐mediated cytotoxicity in 7‐day doxorubicin (H) and nutlin3‐treated (I) cells. n ≥ 2 biological replicates; Doxo‐c1 vs. Doxo RELA RELB‐c1, P = 0.02. Nutlin‐c1 vs. Nutlin RELA RELB‐c1, P = 0.44, n.s.; KS test.