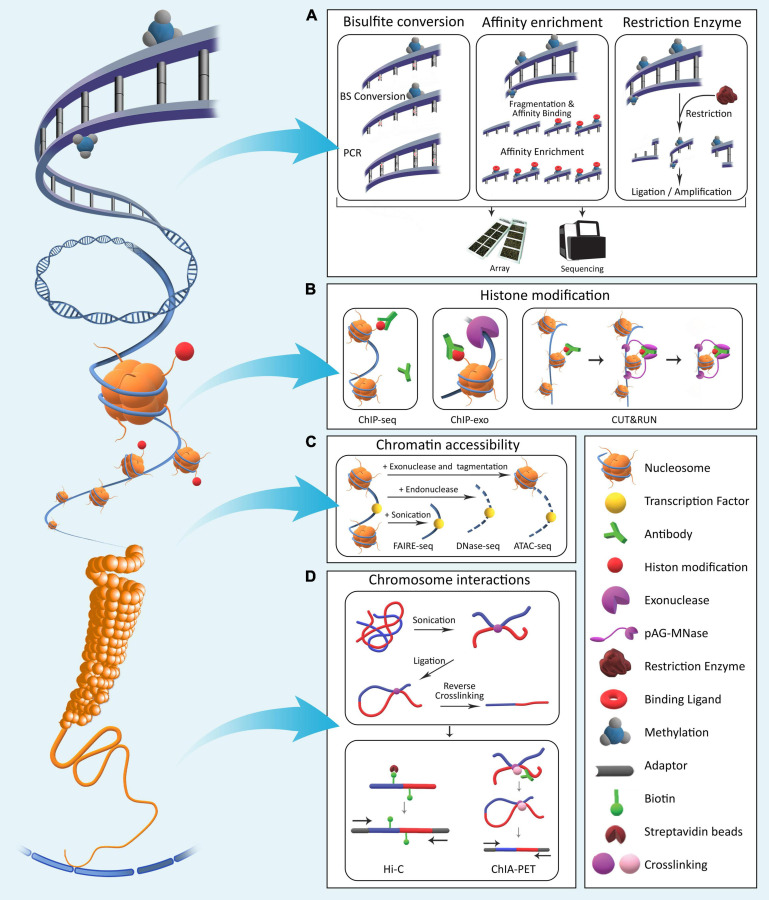
FIGURE 1.
The four major epigenetic layers in Eukaryotic genomes. (A) DNA methylation involves direct chemical addition of a methyl group to certain bases in DNA. Methods for assessment of genome-wide DNA methylation are broadly categorized into bisulfite conversion-based, affinity enrichment-based, and restriction enzyme-based techniques. (B) Histones undergo a variety of chemical modifications on their tail domains. Methods for detection of these modifications rely on antibodies specifically designed to bind modified histone tails for immunoprecipitation with varying levels of resolution. (C) Genomic regions differ with respect to nucleosome occupancy and accessibility of DNA molecule to proteins. Various methods have been developed that quantify these characteristics across the genome. (D) Long-range interactions exist between regulatory elements across the genome. To identify and characterize them in a genome-wide fashion, various methods based on crosslinking and ligation have been developed with varying levels of coverage and specificity (Table 1).