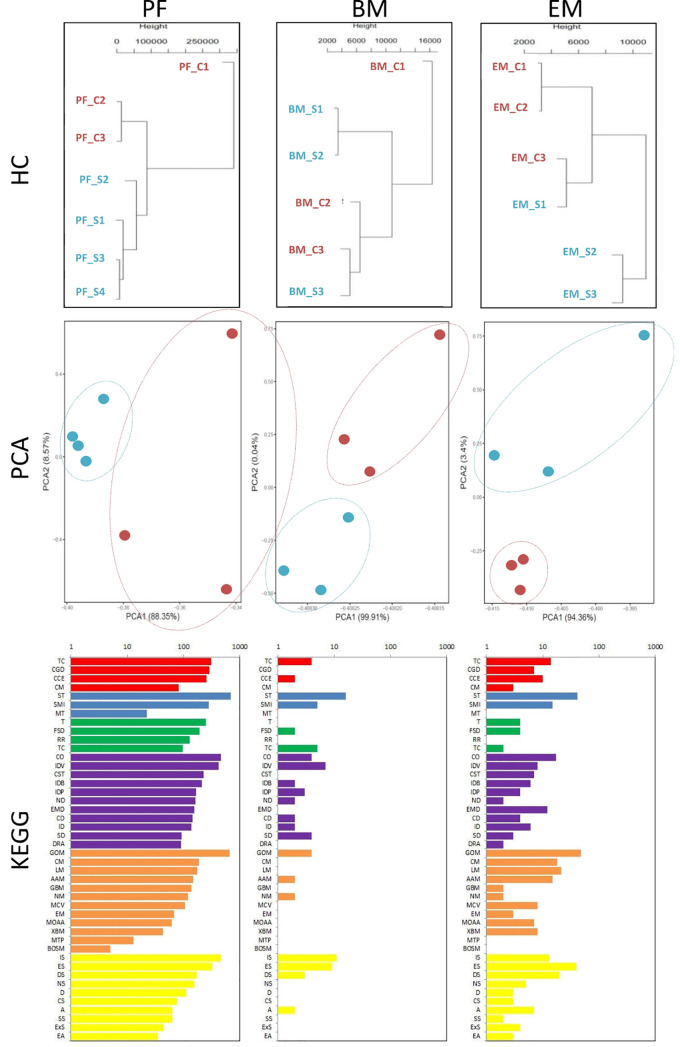
Figure 4.
Transcriptomic characteristics of G-MDSC cells and endometriotic lesions. (Upper and middle panels) Hierarchical clustering (HC) and principal component analysis (PCA) of peritoneal (PF) and bone marrow (BM) CD11b+ Ly6G+ G-MDSCs and endometriosis lesions (EM) from 3-4 animals in each group after 7 days of Sunitinib treatment (S in blue labels and dots) versus control (C in red labels and dots). For HC, the closer the samples were to each other, the more similar the expression level was. For PCA, the first and second most coordinated components are shown, similar transcriptomic profiles were grouped by circles. (Lower panels) KEGG Pathway functional enrichment. X axis represents the number of DEG, Y axis represents the functional classification of KEGG according to 7 branches for KEGG pathways: Cellular Processes (red), Environmental Information Processing (blue), Genetic Information Processing (green), Human Disease (purple), Metabolism (orange), and Organismal Systems (yellow). TC, Transport and catabolism; CGD, Cell growth and death; CCE, Cellular community—eukaryotes; CM, Cell motility; ST, Signal transduction; SMI, Signaling molecules and interaction; MT, membrane transport; T, translation; TS, transcription; CO, Cancer—overview; IDV, infectious diseases—viral; CST, Cancers—specific types; IDB, infectious diseases—bacterial; IDP; infectious diseases—parasitic; ND, neurodegenerative diseases; EMD, endocrine and metabolic diseases; CD, cardiovascular diseases; ID, Immune diseases; SD, substance dependence; DRA, drug resistance—antineoplastic; GOM, Global and overview maps; CM, carbohydrate metabolism; LM, Lipd metabolism; AAM, Amnio acid metabolism; Glycan biosynthesis and metabolism; NM, nucleotide metabolism; MCV, Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins; EM, energy metabolism; MOAA, Metabolism of other amnio acids; XBM, Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism; MTP, Metabolism of tepenoids and polyketides; BOSM, Biosynthesis of other secondary metabolires; IS, Immune system; ES, Endocrine system; DS, Digestive system; NS, Nervous system; D, Development; CS, Cirrculatory system; A, Aging; SS, Sensory system; ExS, Excretory system; EA, Environmental adaptation.