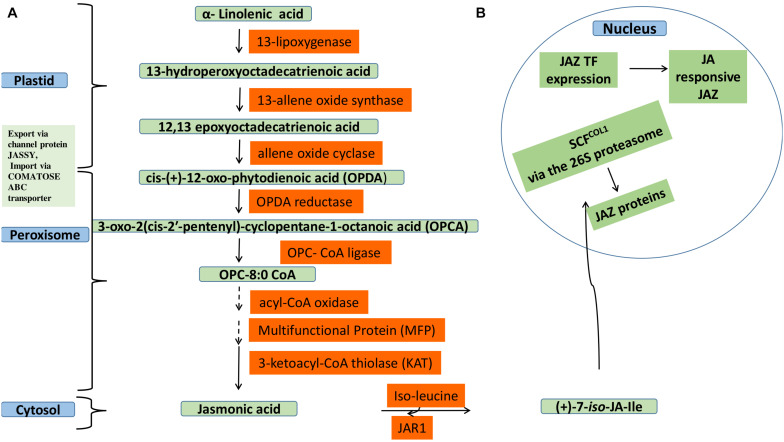
FIGURE 1.
Jasmonic acid biosynthesis and its gene regulation. (A) Jasmonic acid biosynthesis in various cellular compartments involving plastid, peroxisome and cytosol. In plastid α-linolenic acid is converted into 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid that is exported via JASSY channel protein and imported via COMATOSE ABC transporter to peroxisome. Subsequent reduction, β-oxidation, and epimerization reactions lead to JA formation and is released into cytosol. Then JA Conjugates with isoleucine in cytosol to form jasmonoyl–isoleucine (Ile-JA). (B) Degradation of JAZ repressor proteins via SCFCOI1 regulating JA gene expression at transcription level Ile-JA is in turn perceived Skip-Cullin–F-box complex (SCFCOI1) which mediates degradation of the JAZ repressor via 26S proteasome degradation, thereby relieving the repression by JAZ, transcriptional regulator.