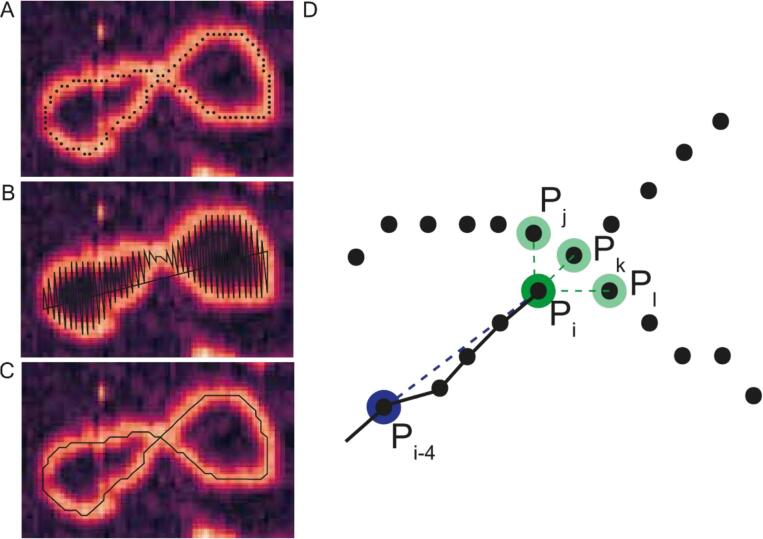
Fig. 4.
Schematic showing how the ordering process works. (A) An example image showing the pixelated binary skeleton. (B) The initial “disordered” trace in which coordinates are listed in ascending order based on the x-coordinate. Note how this trace does not follow the contours of the molecule. (C) The ordered trace that now follows the direction of the underlying molecule. (D) Diagrammatic representation of the angular search algorithm used to select the next point in the trace when multiple candidates are available. The point Pi is the reference point, and the reference angle is calculated using the vector between points Pi-4 and Pi. To distinguish between the candidate points, Pj, Pk and Pl, the angle between each candidate point and the reference point Pi-4 is calculated. The candidate point with the vector angle most similar to that between Pi and Pi-4 is accepted as the next point in the trace.