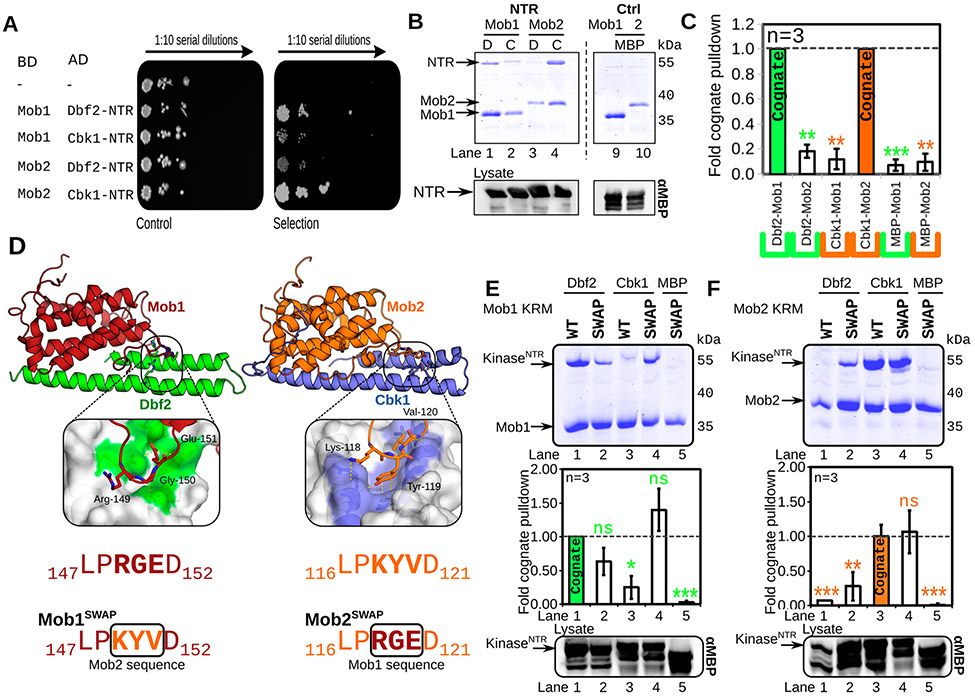
Figure 4.
Ndr/Lats–Mob binding is specific and controlled through a three-residue motif. (A) Mob–NTR interaction specificity is maintained in vivo. Yeast two-hybrid test of kinase–NTR complexes. Selection: yeast cells containing binding domain (BD)–Mob and activation domain (AD)–NTR fragments on dropout agar serially diluted. Growth on this “Selection” agar plate is indicative of binding between BD and AD constructs (BD, DNA-binding domain construct; AD, transcriptional activation domain construct; −, empty plasmid). Viability/growth “Control” plate: single AD construct transformants grown on nonselective YPD agar plates. (B) Dbf2 and Cbk1 form specific complexes with Mob1 and Mob2, respectively, in vitro. MBP-fused Dbf2 NTR (85–173), labeled as “D”, and Cbk1NTR (251–351), labeled as “C”, were co-expressed with His6-fused Mob1 and Mob2 V148C Y153C in E. coli, isolated via nickel chromatography, separated via SDS–PAGE, and stained with Coomassie. The dotted line demarcates a division in the gel. Bottom panels show Western blots of the E. coli lysate using anti-MBP antibody (αMBP). NTR, intact MBP–NTR fusion. (C) Quantification of panel B. The Coomassie signal from prey Dbf2–Cbk1 was normalized to the amount in the total lysate and divided by the total bait signal. Three individual replicates were performed. Samples were normalized to the “cognate” Dbf2–Mob1 (green) or Cbk1–Mob2 (orange) signals [ns, p > 0.05; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; or ****p < 0.0001, based on a two-tailed t test (n = 3)]. (D) Diagram of wild-type (WT) and “swapped” Mob cofactors. The kinase restrictor motif (KRM), a short, three-amino acid motif at the interaction interface (purple) between Mob and the kinase NTR, was mutated to reflect the paralogous sequence in Mob1 and Mob2. Mob1SWAP was mutated to possess the Mob2 sequence (KYV); Mob2SWAP has the KRM mutated to the Mob1 sequence (RGE). (E and F) Mob1SWAP and Mob2SWAP mutants gain the ability to bind noncognate kinases. in the top panels, wild-type (WT) or His6-fused swapped (SWAP) Mob1 (E) or Mob2 (F) was co-expressed with MBP-fused Dbf2 or Cbk1 NTR in E. coli, isolated via nickel chromatography, separated via SDS–PAGE, and stained with Coomassie. The middle panels show the quantification of the top panels as in panel B. The bottom panels show Western blots of the E. coli lysate using the anti-MBP antibody (αMBP). KinaseNTR, intact MBP–NTR fusion.