Figure 2.
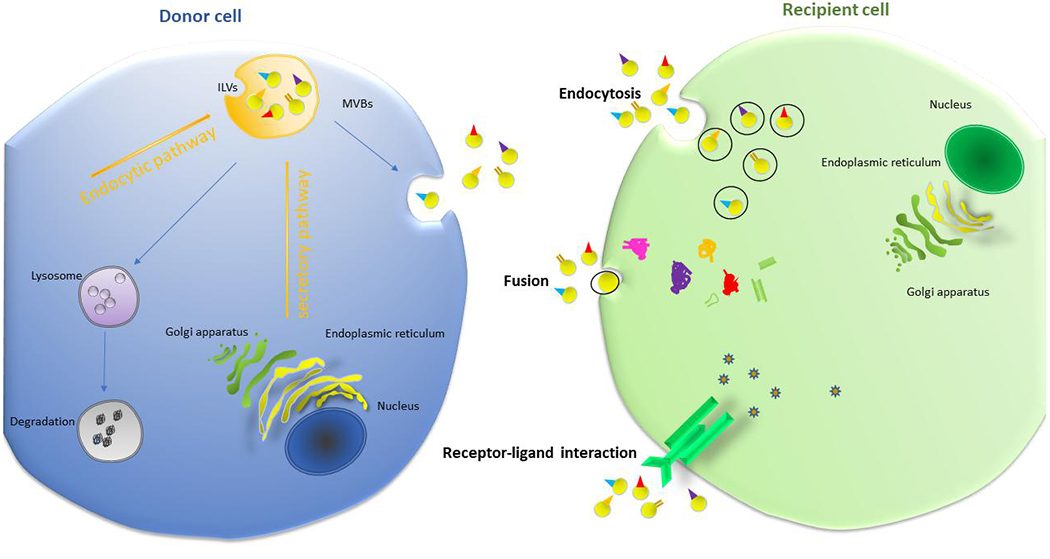
Biogenesis of exosome. The biogenesis of exosomes occurs when multivesicular bodies uptake intraluminal vesicles formed from either endocytic pathway or ER/Golgi secretory pathway. Then, MVBs either fuse with cellular membrane to release exosomes, or fuse with lysosomes for cargo degradation. After releasing into extracellular space, exosomes act as a mediator of intercellular communication through being taken up by recipient cells via endocytosis, fusion or receptor-ligand interaction. This process can be either paracrine or endocrine in manner. MVBs: Multivesicular bodies.
