Fig. 1.
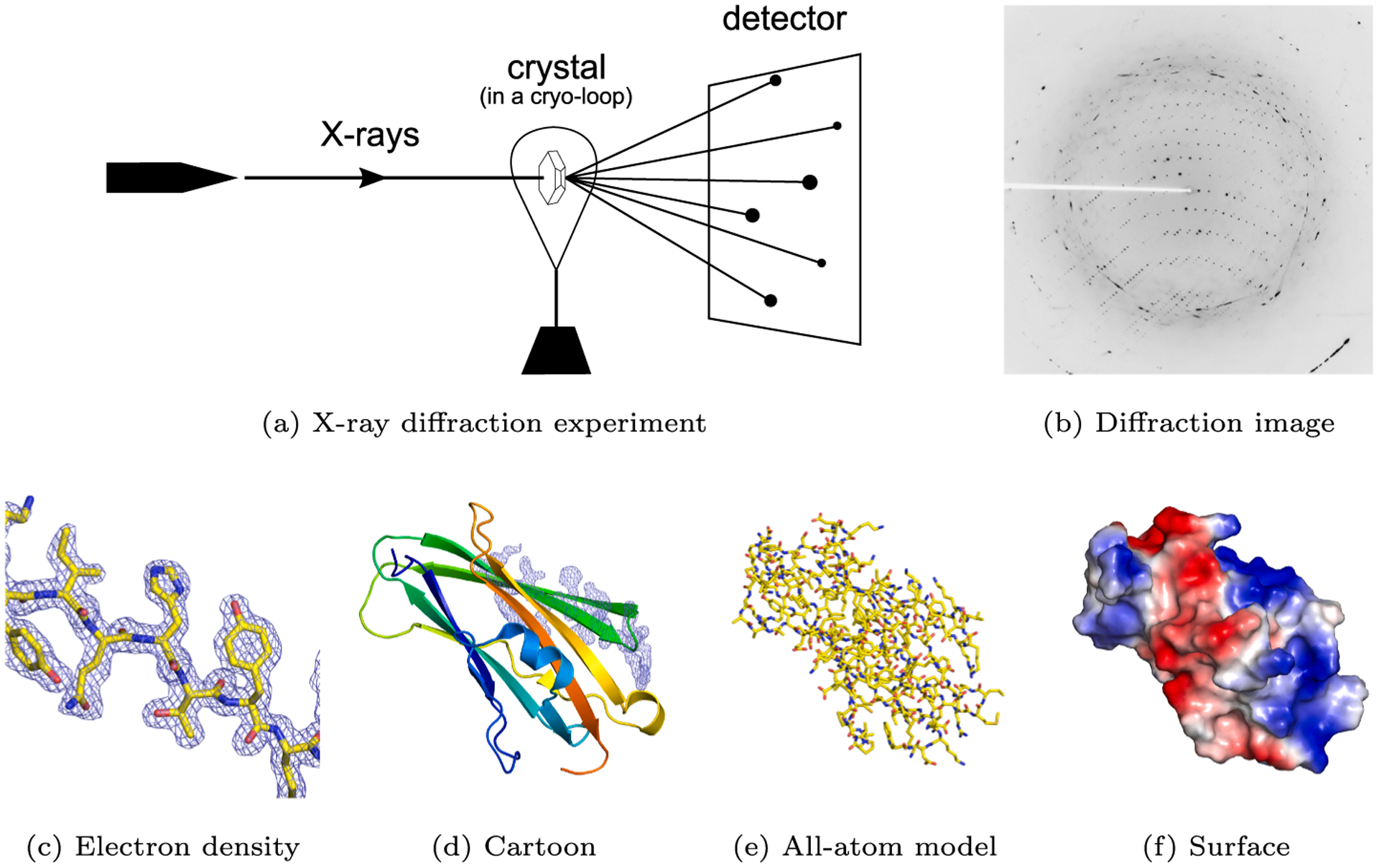
The principle of crystallography (Mayer, 2017). (a) An X-ray beam hits a crystal. (b) The observed diffraction spots (X-ray diffraction image) are the result of the interaction of diffracted photons with the active area of the detector. (c) A fragment of electron density with the associated molecular model of a RhoGDI-mutant protein (PDB code: 2JHU Cooper et al., 2007). (d) A cartoon representation of the entire protein, with the same electron density fragment as on the left. (e) An all-atom representation colored by atom type. (f) A surface representation colored by electrostatic potential.
