Figure 7. Associations between hepatic GABA system and glucoregulatory markers in obese humans.
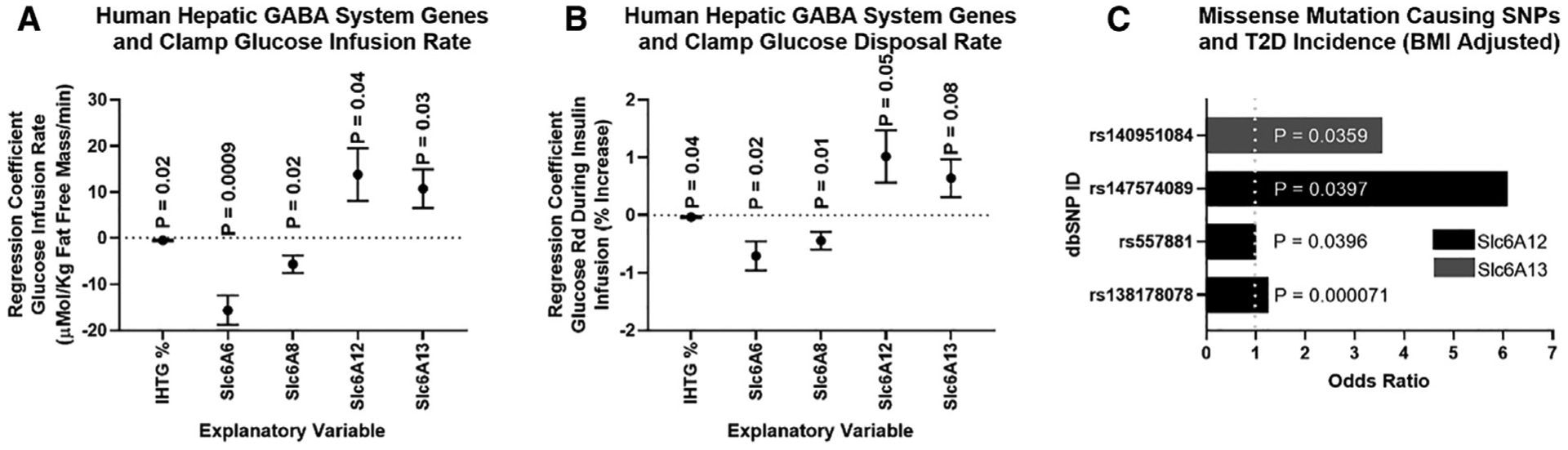
(A and B) Multivariate regressions including intrahepatic triglyceride % (IHTG%) and the mRNA for the hepatic GABA transporters (Slc6A6, Slc6A8, Slc6A12, and Scl6A12) as explanatory variables for variations in glucose infusion rate during a hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp (μMol/kg fat-free mass/min) (A), and the glucose disposal rate calculated during a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp (Glucose Rd, % increase) (B). mRNA (fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads [FPKMs]) was quantified by RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) from liver tissue.
(C) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that cause missense mutations in Slc6A12 or Slc6A13 are associated with an increased incidence of type 2 diabetes (T2D) adjusted for body mass index (BMI). Regression data are presented as mean ± SEM.
