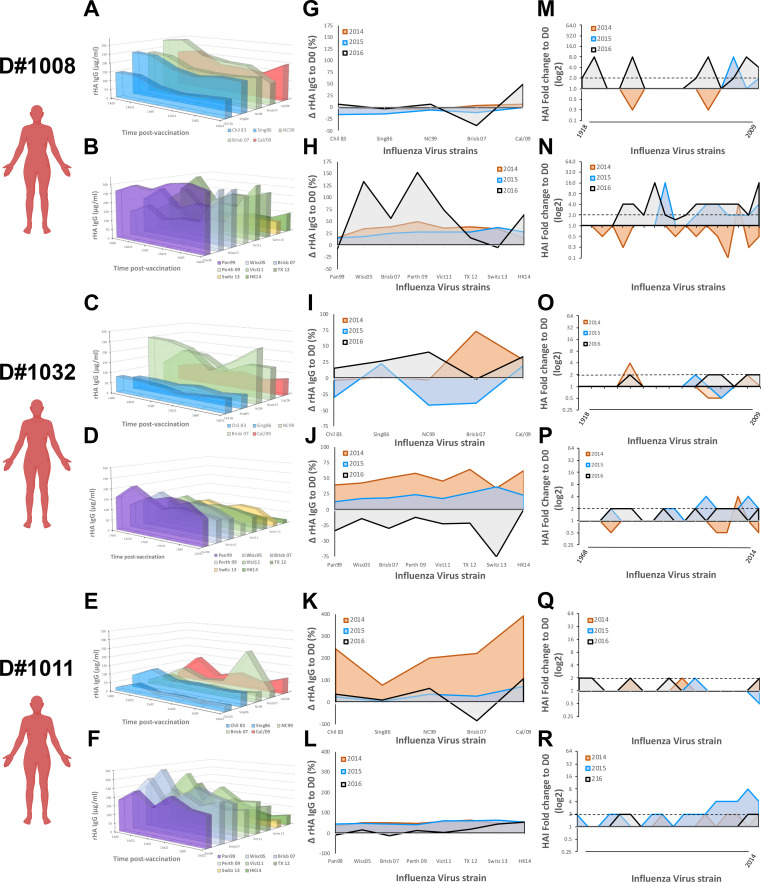
Fig 4. Serological antibody landscape in young participants vaccinated for three consecutive years.
A,C,E) Serological IgG antibodies against rHA from current H1N1 vaccine strain and 4 historical seasonal H1N1 virus strains (1983–2007) in three young participants vaccinated for three consecutive years. Colors represent antigenically similarity between H1 rHA. B,D,F) Serological IgG antibody levels against rHA the current H3N2 vaccine strains and 5 historical seasonal H3N2 virus strains (1999–2011) in three young participants vaccinated for three consecutive years. Colors represent antigenically similarity between H3 rHA. G,I,K) Changes in serological antibody levels against rHA from different H1N1 virus strains, measured as in A, 21–28 days after vaccination in young participants vaccinated for three consecutive years. H,J,L) Changes in serological antibody levels against rHA from different H3N2 virus strains, measured as in B, 21–28 days after vaccination in young participants vaccinated for three consecutive years. M,O,Q) Changes in serological HAI activity titer against different H1N1 virus strains (1918–2009) 21–28 days after vaccination in young participants vaccinated for three consecutive years. N,P,R) Changes in serological HAI activity titer against different H3N2 virus strains (1968–2016) 21–28 days after vaccination in young participants vaccinated for three consecutive years.