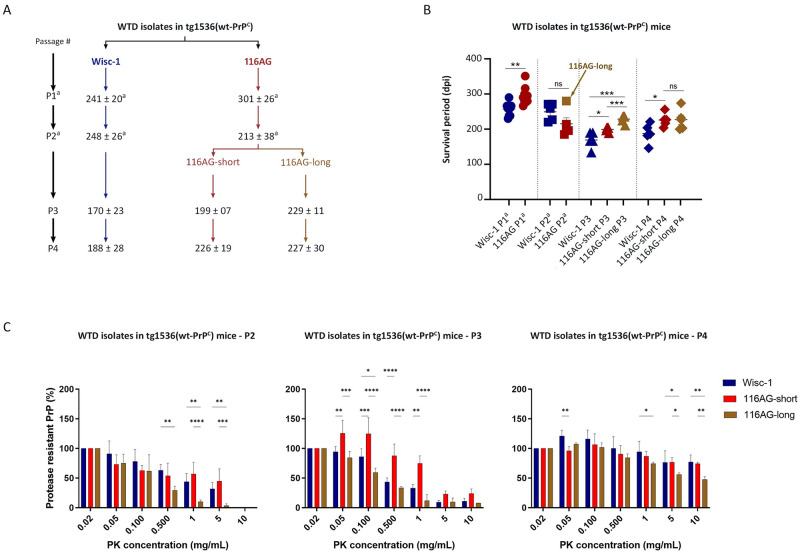
Fig 1. Serial transmission of Wisc-1 and 116AG isolates in tg1536+/+ mice.
Tg1536+/+ mice, overexpressing wt deer PrP 6 to 8fold, were inoculated intracerebrally with 20ul of 1% (w/v) brain homogenate. (A) Scheme of the serial transmission (1st ➔ 4th passage) of Wisc-1 and 116AG isolates to tg1536+/+ mice, mean survival times with standard deviation are shown. (B) Representative graph of the survival times of tg1536+/+ mice inoculated with Wisc-1 or 116AG prions. The y-axis represents the survival period (dpi) and the x-axis the different passages. Wisc-1 inoculated mice are represented by blue shapes and 116AG inoculated mice are represented by red shapes (filled for 116AG-short and open for 116AG-long). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ns p > 0.05; unpaired student’s t-test was used to compare between different groups of mice. (C) Resistance to PK was assessed using different concentrations of PK to digest brain homogenates of WTD passaged isolates in tg1536 mice (P2, P3 and P4 represent second, third and fourth passage). The PrPres signal was quantified by densitometric and blotted into graphs using GraphPad Prism software for analyses. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001 refers to differences between PK resistance of Wisc-1 (blue bars), 116AG-short (red bars) and 116AG-long (brown bars). Statistical analyses were performed using two-way ANOVA followed by post hoc (Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; GraphPad Prism software). a data from Hannaoui et al. [26].