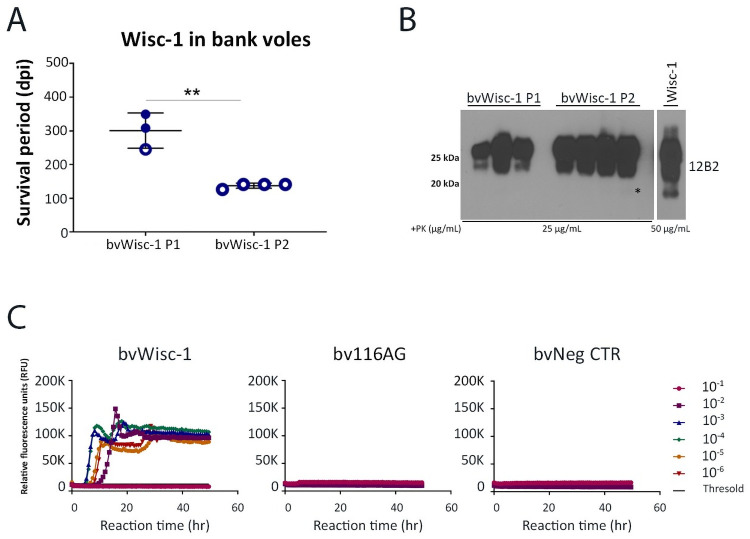
Fig 3. Transmission of Wisc-1 or 116AG prion isolates to bank voles.
Inoculations of bank voles were performed through the intracerebral route using 20 ul of 1% (w/v) brain homogenate. (A) Survival times of bank voles upon inoculation with Wisc-1 prions upon first and second passage. None of the animals inoculated with 116AG prions showed prion disease signs upon experimental endpoint (700 dpi). **p <0.01, statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired student’s t-test. (B) Western blot using mAb 12B2 (aa 93 to 97) depicting PrPres in brain homogenates of bank voles inoculated with Wisc-1 upon first passage (lanes 1–3), second passage (lanes 5–8) and Wisc-1 original isolate (lane 10; the illustrated blot is less exposed than that of 1st and 2nd passage PrPres). (C) RT-QuIC reactions were seeded with serially diluted (10−1 to 10−6) brain homogenates from bank voles inoculated with Wisc-1 (left panel) and 116AG (center panel) prions using rPrP bank vole substrate. Negative control is shown on the right panel. Fluorescence was measured every 15 min. The y-axis represents the relative fluorescence units (RFUs) and the x-axis the reaction time (hours). Each curve represents a different dilution and mean values of four replicates were plotted for each dilution. Reactions were positive when the mean RFU crossed the threshold (determined by averaging the RFUs of the negative control +5 SD).