| Phenyl |
1 |
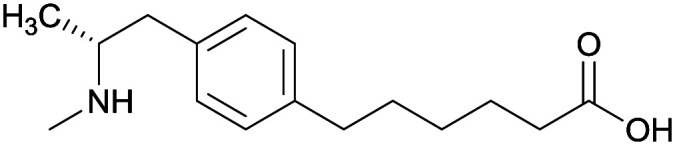
|
KLH |
Alum |
SC |
3 injections/6 weeks |
Locomotor activity |
No differences between METH-challenged and non-challenged groups in generating antibody titer and affinity. Failed to attenuate hyperlocomotion |
65
|
| 2 |
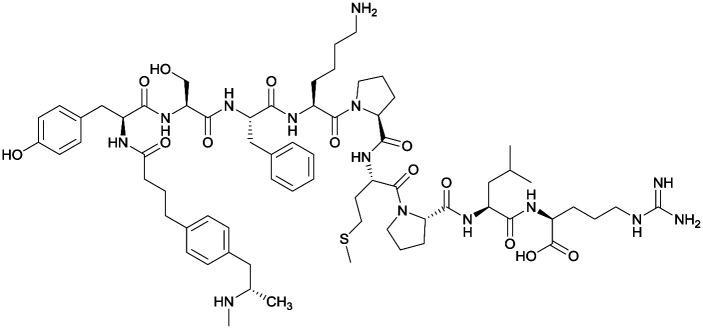
|
None |
EP54 (peptide) |
SC and IP |
5 injections/5 weeks |
Self-administration |
Antibody titers were highest in vaccine 3, then vaccine 5, followed by similar levels generated for vaccine 2 and 4. The antibodies generated for vaccine 3 showed high specificity. Self-administration studies showed compensatory effects in vaccinated animals, leading to increased drug intake |
72
|
| 3 |
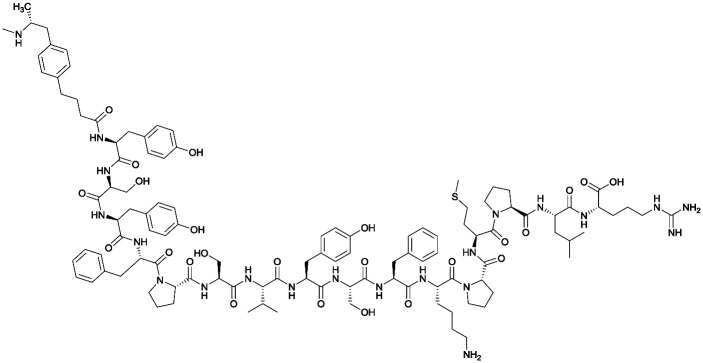
|
TT |
| 4 |
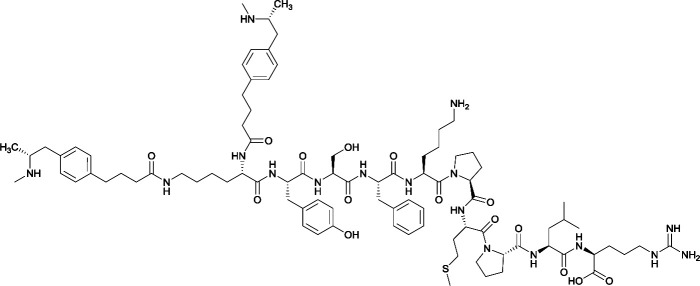
|
None |
| 5 |
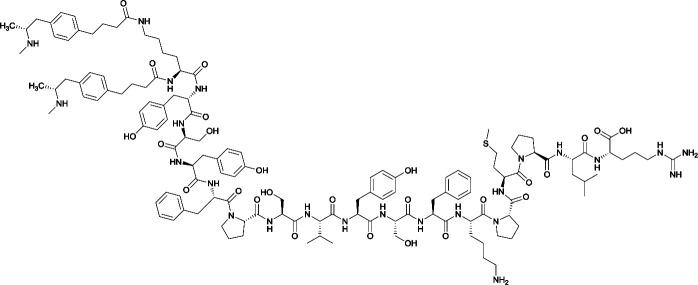
|
TT |
| 6 |
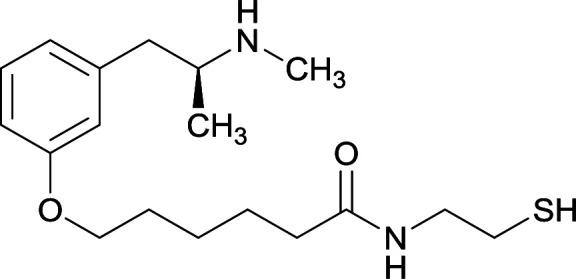
|
OVA and BSA |
Freund's complete adjuvant |
SC |
3 injections/6 weeks |
None |
Vaccine 6 produced a significantly higher immune response by providing high epitope densities on maleimide-activated proteins. |
73
|
| 7 |
Same structure as vaccine 6 |
KLH |
Alhydrogel |
SC |
4 injections/12 weeks |
Food maintained behaviour |
The vaccine reduced effects induced by high doses of METH through high affinity antibodies |
66
|
| 8 |
Same structure as vaccine 6 |
KLH |
Alhydrogel vs. Sigma Adjuvant System vs. GLA-SE |
IM |
3 injections/9 weeks |
None |
GLA-SE produced double the antibody concentration with enhanced affinities against METH. Significantly, these results were sustained without boosts |
74
|
| 9 |
Same structure as vaccine 6 |
KLH |
Sigma Adjuvant System |
SC |
4 injections/15 weeks |
Blood–brain biodistribution |
Vaccine 10 showed significant increases in METH sera concentrations in vaccinated animals and decreases in brain concentrations, compared to passive immunization |
64
|
| 10 |
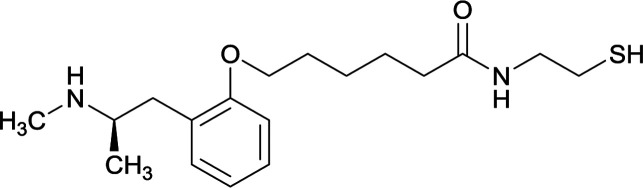
|
| Methyl |
11 |
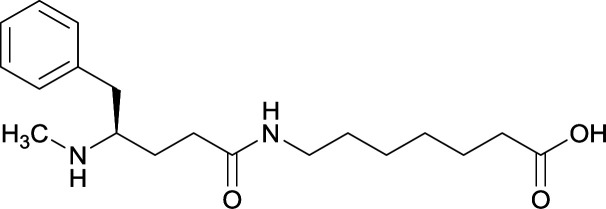
|
TT |
Alum and CpG ODN 1826 |
IP |
3 injections/4 weeks |
Locomotor activity, blood–brain biodistribution, and lethality challenge |
All stereoisomers generated antibodies that could affect blood–brain drug partitioning. However, vaccine 12 produced antibodies with 10-fold higher affinities, compared to single isomers and racemate. Only vaccine 12 effectively attenuated METH-induced hyperlocomotion. Lethality studies for vaccine 11, 13, and 12 exhibited survival rates of 16.7%, 33.3% and 83.3%, respectively |
56
|
| 12 |
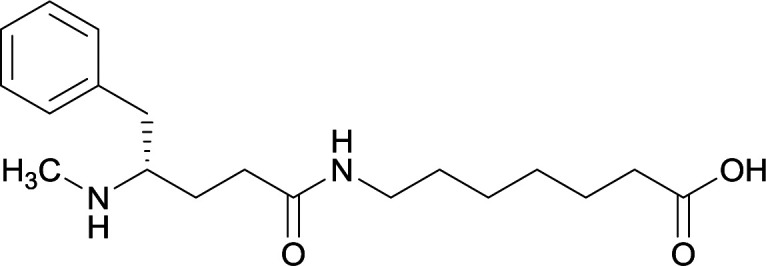
|
| 13 |
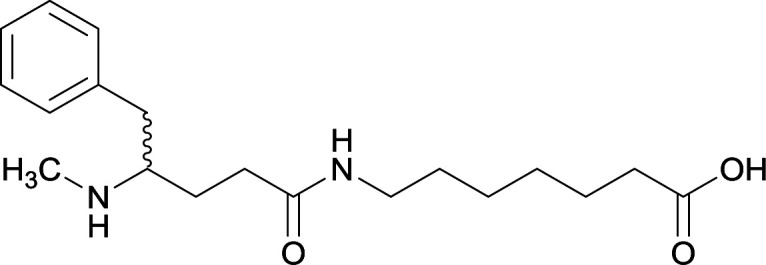
|
|
N-methyl |
14 |
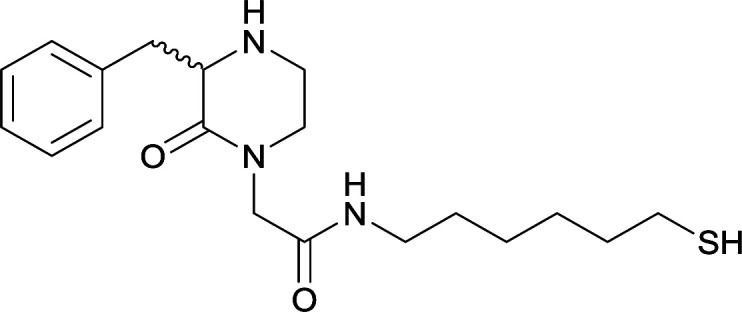
|
KLH or BSA |
Sigma Adjuvant System |
IP |
3 injections/5 weeks |
None |
Vaccines 15, 18, and 19 were able to successfully induce increased levels of high affinity antibodies in murine models, with vaccine 15 and 19 producing antibodies with specificities toward METH and amphetamine. Vaccine 18 and 19 produced the highest titers |
75
|
| 15 |
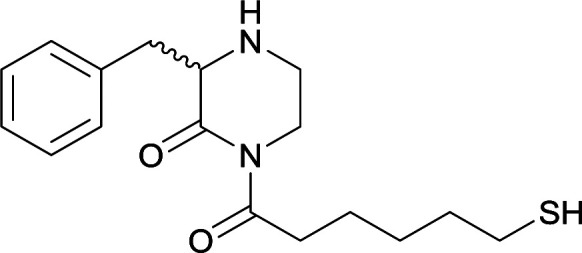
|
| 16 |
|
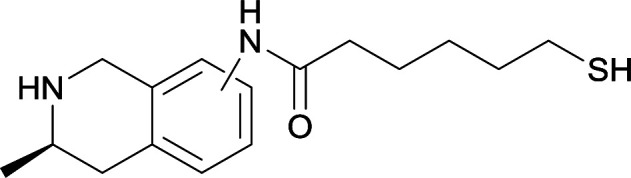
| 17 |
|
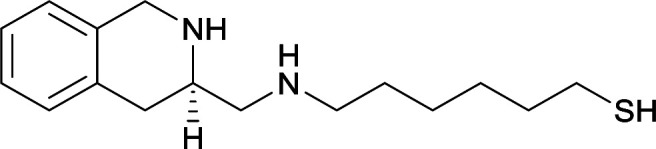
| 18 |
|
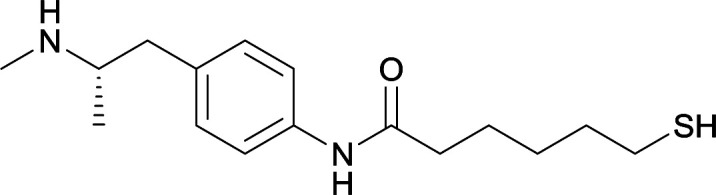
| 19 |
|
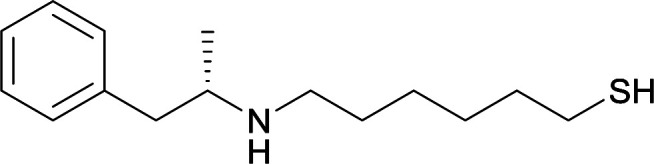
| 20 |
Same structure as vaccine 19 |
KLH |
Sigma Adjuvant System |
SC and IP |
4 injections/9 weeks |
Thermoregulation, wheel activity, locomotor activity, and blood–brain biodistribution |
The vaccine attenuated METH-induced thermoregulatory and locomotor responses. Pharmacokinetics showed the vaccine produced higher drug concentrations in sera and lower METH presence in the brain after exposure to drugs |
62
|
| 21 |
Same structure as vaccine 19 |
KLH |
Sigma adjuvant system |
SC and IP |
3 injections/5 weeks or 5 injections/13 weeks |
Self-administration and acute challenge |
The vaccine attenuated self-administration at 0.1 mg per kg. Plasma METH concentrations were increased in vaccinated groups after drug challenges |
76
|
| 22 |
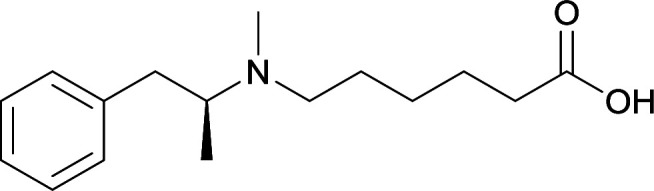
|
DT and BSA |
Lipid Tucaresol |
SC |
3 injections/5 weeks |
None |
Vaccines with lipid tucaresol induced antibodies with higher specificity |
77
|
| 23 |
Same structure as vaccine 22 |
DT |
Sigma adjuvant system |
SC |
3 injections/5 weeks |
Locomotor activity |
Vaccines 24 and 25 produced antibodies with comparable affinities, but vaccine 25, containing peptidic linkers, enhanced antibody concentration. Vaccine 29 elicited higher affinity antibodies, but produced drastically lower titers. Thus, the vaccine was optimized by changing the carrier protein and adjuvant cocktail, which generated antibodies with exceptionally high titers and abilities to attenuate METH-induced locomotor effects |
78
|
| 24 |
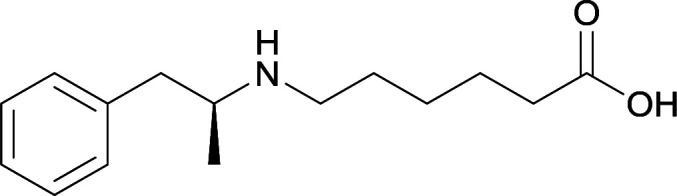
|
| 25 |
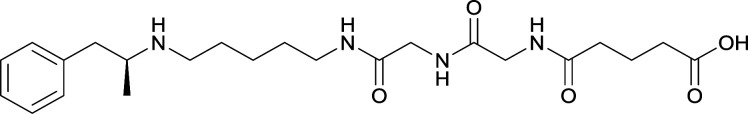
|
| 26 |
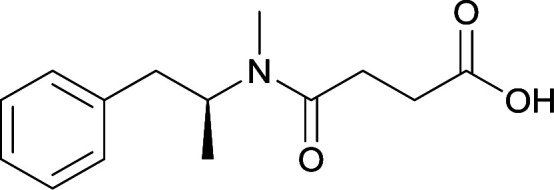
|
| 27 |
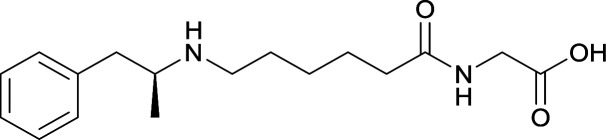
|
| 28 |
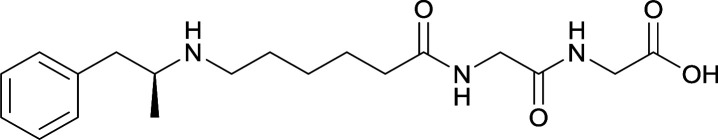
|
| 29 |
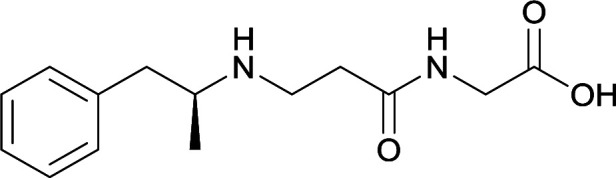
|
| 30 |
Same structure as vaccine 29 |
TT |
Alum and CpG ODN 1826 |
|
3 injections/4 weeks |
| 31 |
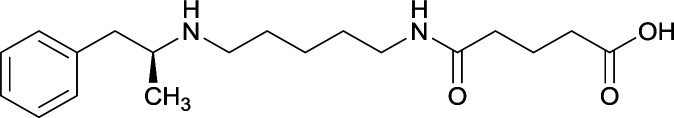
|
KLH or TT |
Alum and CpG ODN 1826 |
IP |
3 injections/4 weeks |
Blood–brain biodistribution |
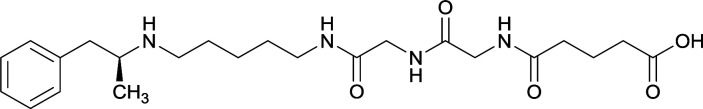
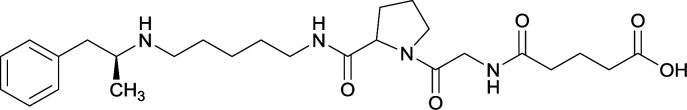
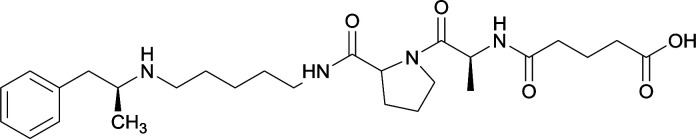
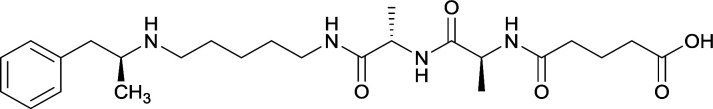
Vaccines 32, 33, 34, and 35 induced antibodies with increased drug affinity, but lower concentrations than control vaccine 31. Since vaccine 35 generated the highest titers, vaccine 36 and 37 were probed for antibody effects. Both elicited antibodies with similar affinities to vaccine 35, but generated increased titers. Vaccine 36 was the most efficient in attenuating drug CNS interaction |
79
|
| 32 |
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
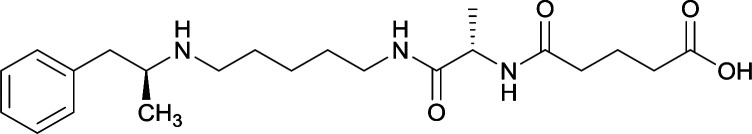
|
| 37 |
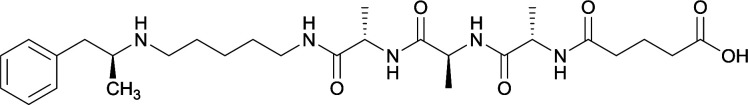
|
| 38 |
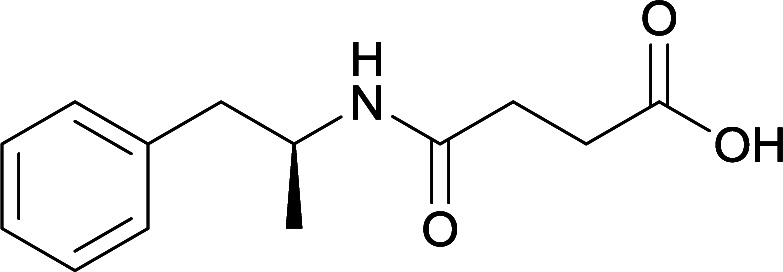
|
KLH |
MPLA |
SC |
3 injections/20 weeks |
Locomotor activity and conditioned place preference |
The vaccine generated antibodies at high titers, reduced drug-conditioned approach behaviours, and attenuated METH-induced locomotion at varying doses |
80
|
| 39 |
same structure as vaccine 38 |
TT |
Alum |
IM |
2 injections/3 weeks |
conditioned place preference |
The vaccine produced higher and sustained antibody concentrations that decreased drug entry into the brain and inhibited METH acquisition and reinstatement |
63
|
| 40 |
Same structure as vaccine 38 |
TT |
E6020 and Alum |
SC |
3 injections/6 weeks |
Locomotor activity and blood–brain biodistribution |
Vaccines with E6020 produced x3 increase in titers, nanomolar affinities, attenuated METH-induced hyperlocomotion, and decreased brain METH levels while increasing drug sera concentration |
81
|































