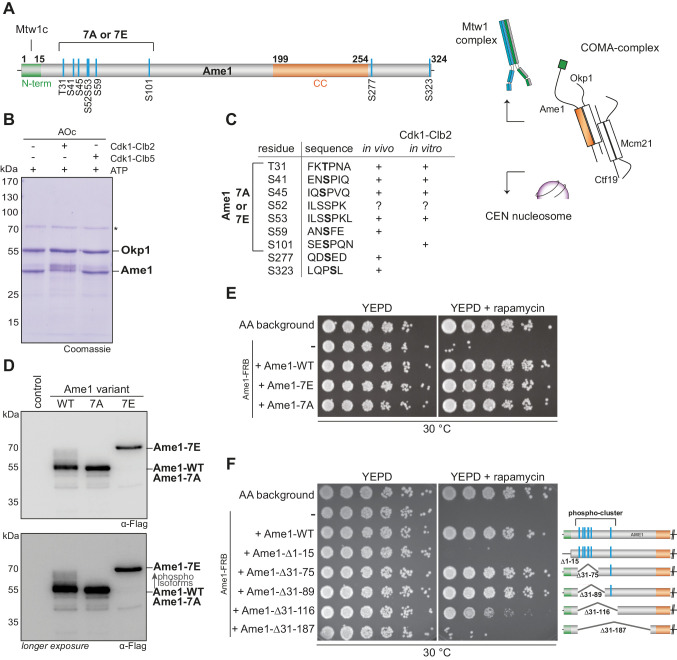
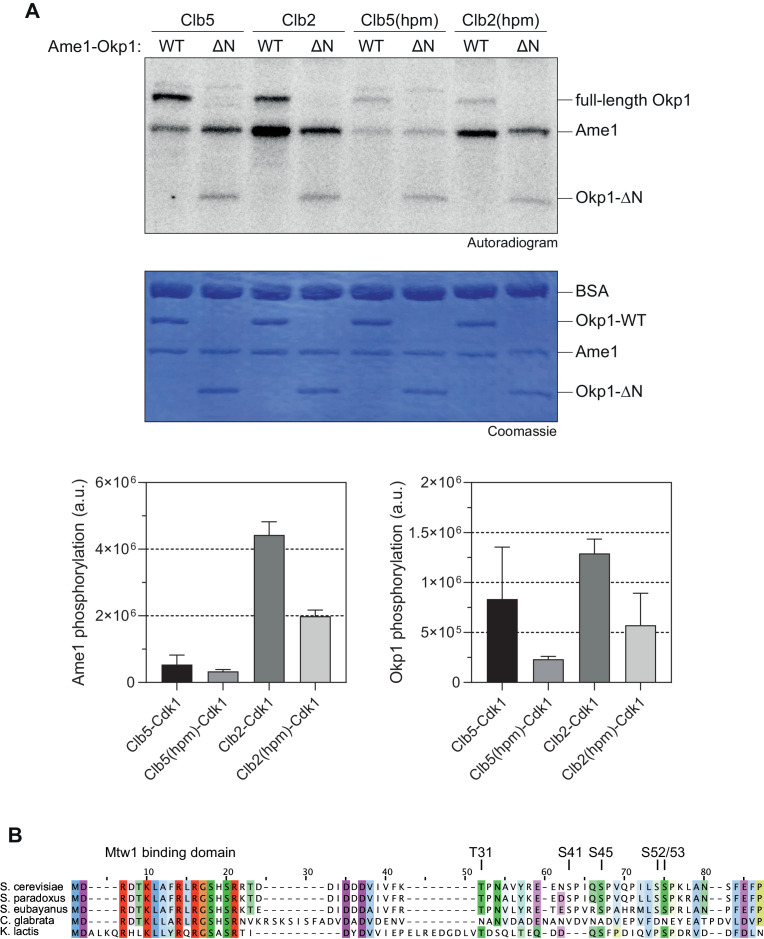
Figure 1. Phosphorylation analysis of the essential constitutive centromere-associated network (CCAN) subunit Ame1.
(A) Organization of the essential CCAN component Ame1CENP-U and localization of phosphorylation sites. Ame1 shows a Cdk1 phosphorylation cluster (T31, S41, S45, S52, S53, S59, S101) at the N-terminus. The first 15 amino acids are essential for Mtw1c binding, the coiled-coil region (aa 199–254) is required for heterodimerization with Okp1CENP-Q. Schematic overview on the right shows the four-protein complex COMA, consisting of Ame1CENP-U, Okp1CENP-Q, Ctf19CENP-P, and Mcm21CENP-O. The COMA complex binds to the outer kinetochore component Mtw1 complex and to the centromeric nucleosome. (B) In vitro kinase assay with recombinant Ame1-Okp1c with either Cdk1-Clb2 or Cdk1-Clb5. The migration pattern of Ame1 is shifted to a slowly migrating form when incubated with Cdk1-Clb2. Asterisk denotes a contaminating protein. (C) List of all mapped Ame1 phosphorylation sites either in vivo or in vitro. T31, S41, S45, S53, and S101 show the minimal motif for Cdk1 (S/TP). (D) Stably integrated Ame1 variants display distinct migration patterns in SDS-PAGE. Ame1-WT shows multiple slowly migrating forms that are eliminated in Ame1-7A and Ame1-7E. (E) Serial dilution assay of Ame1 variants using the FRB anchor-away system. Ame1-WT and both mutants can rescue the growth defect when endogenous Ame1 is anchored away from the nucleus. (F) Serial dilution assay of internal Ame1 truncation mutants in the anchor-away system.