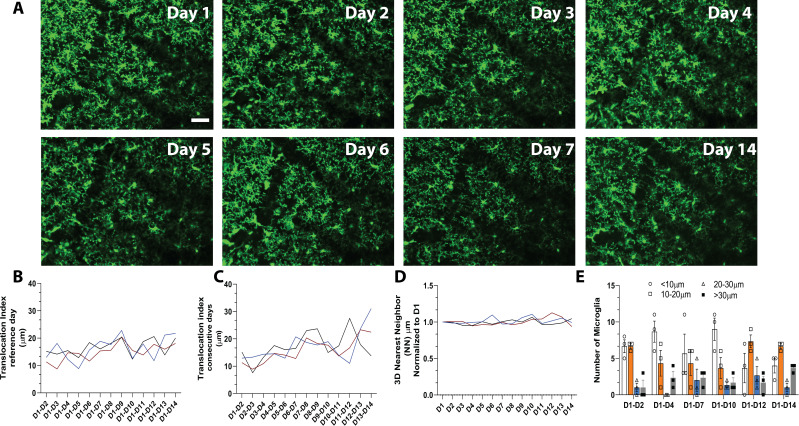
Figure 1. In vivo imaging of microglia shows limited migration and turnover in the physiological brain.
(A) A field of microglia in an awake mouse imaged over 14 consecutive days. The dark diagonal lines in the center and top right of the image are blood vessels that remain structurally stable and can be used as landmarks to identify the same location for chronic imaging. Several microglia are identified with the same-colored circles at different time points to show the stability of their somas. (B) Nearest neighbor quantification in 3D demonstrates the distribution of neighboring microglial cells over consecutive days. (C) The translocation index, which captured the average displacement of microglia over time, was ~15 µm when consecutive imaging sessions were compared. (D) The translocation index increased when D1 is compared to imaging carried out later (D2–D14). (E) Microglia translocation between D1-D2, D1-D4, D1-D7, D1-D10, D1-D12, and D1-D14. On average, the majority of microglia remained within ~10 µm away (white bars, circles) from their original location. The number of microglia that moved within their domain (10–30 µm; orange bars, squares), (20–30 µm; blue bars, triangles) or translocated a further distance (>30 µm; gray bars, filled circles) stayed relatively constant with increasing interval between imaging sessions (n=3, 30–40 µm stacks, 13–17 microglia per mouse). Scale bar, 50 μm. Figure 1—source data 1: Source data for microglia turnover and migration in the physiological brain.