Figure 2.
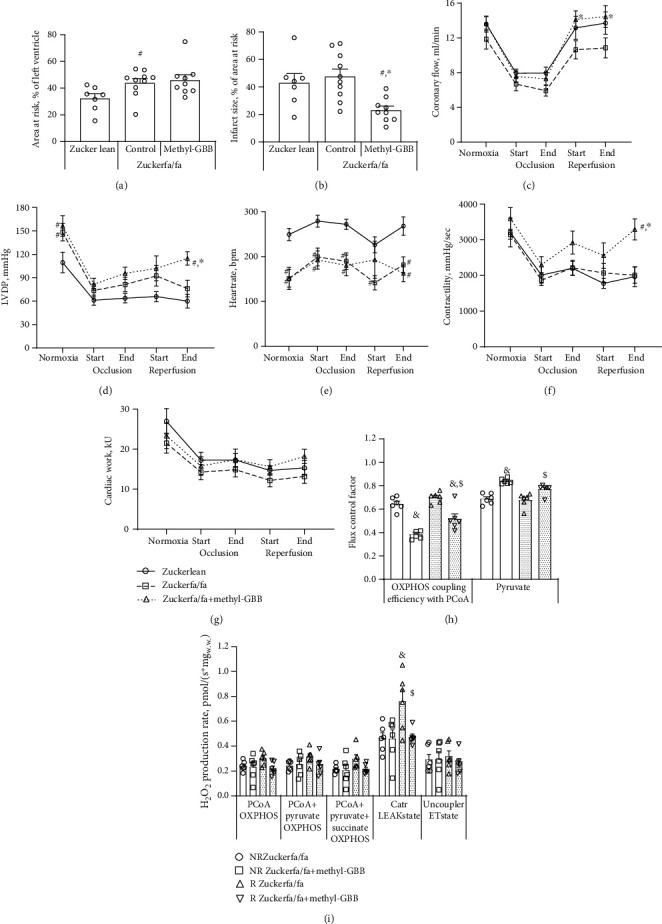
The effect of methyl-GBB administration on myocardial infarct size (a, b) and heart functional parameters (c–g) in Langendorff-perfused isolated hearts and the flux control factor (h) and mitochondrial ROS production (i) in permeabilized cardiac fibres from normoxic nonrisk (NR) and reperfused area at risk (R) regions of the heart after 12 weeks of treatment. Each value was calculated as the mean ± S.E.M. of 7 hearts in the Zucker lean group, 9 hearts in the methyl-GBB-treated group, and 10 hearts in the Zucker fa/fa control group for (a) and (b) and 8(7) hearts for (c–g), and 6 hearts for (h) and (i). ∗Significantly different from the Zucker fa/fa control group; #significantly different from the Zucker lean rat group (Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test; P < 0.05 for (a), ANOVA followed by Tukey's test; P < 0.05 for (b), two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test; P < 0.05 for (c–g)). $Significantly different from the respective Zucker fa/fa control (NR or R) group. &Significantly different from the respective normoxic (NR) group (ANOVA followed by Tukey's test; P < 0.05).
