Figure 5.
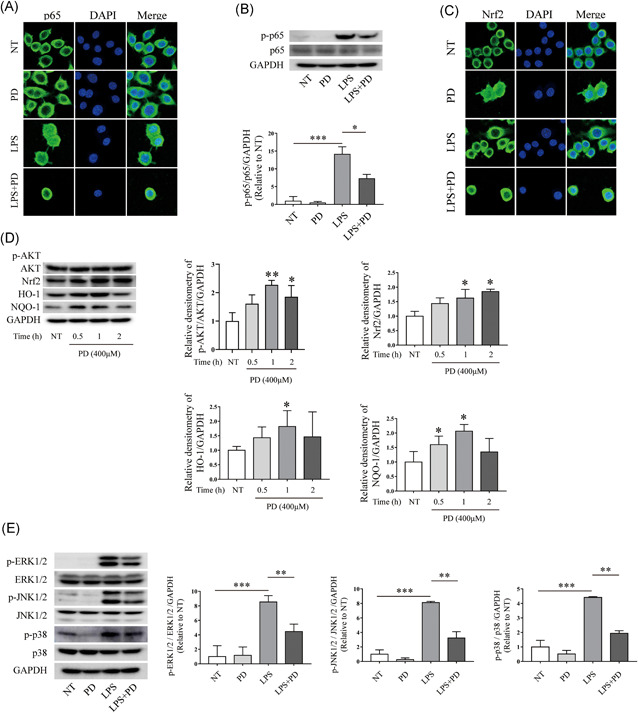
PD inhibited the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of NF‐κB p65 signaling pathway. PD was used to treated RAW264.7 cells for 1 h followed by stimulating using LPS (1 μg/ml) for 1 h. (A) Cell immunofluorescence was performed to evaluate nuclear translocation of NF‐kB p65 signaling pathway, magnification is ×63 (n = 3). (B) After treatment with PD and LPS, Western blot was used to determine the phosphorylation of NF‐κB p65 signaling pathway (n = 3). (C) RAW264.7 cells were treated using PD for 1 h followed by stimulating using LPS (1 μg/ml) for 1 h. Cell immunofluorescence analyses the nuclear translocation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway, magnification is ×63 (n = 3). (D) RAW264.7 cells were stimulated with PD (400 μM) for 0.5, 1, and 2 h. Total protein was extracted from PD treated cells and used to determine the phosphorylation of AKT signaling pathway, and the expression level of Nrf2, HO‐1, and NQO‐1 (n = 3). (E) PD was used to treat RAW264.7 cells 1 h followed by treating using LPS (1 μg/ml) for 1 h. Protein was extracted from RAW264 cells and used to determine the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, JNK1/2, and p38 signaling pathway. PD treatment inhibited the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, JNK1/2, and p38 signaling pathway (n = 3). ERK, extracellular signal‐regulated kinase; JNK, c‐Jun N‐terminal kinase; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NF‐κB, nuclear factor‐κB; PD, polydatin. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001
