Figure 2. The mechanisms involved in the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway: the “hinge and latch” model.
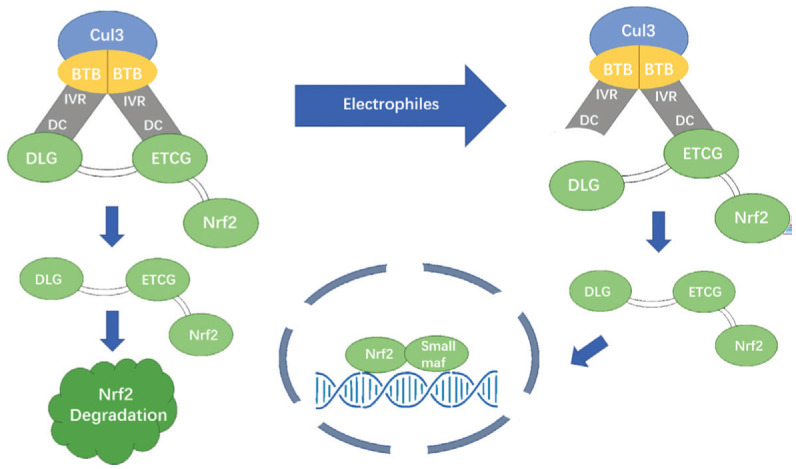
The ETGE and DLG motifs in the Neh2 domains bind to Keap1's DC domain with different affinities. Under normal circumstances, Nrf2 is isolated in the cytosol and keeps a low level through Keap1-dependent ubiquitination and protease degradation. Under oxidative stress, electrophiles (such as ROS) covalently modify the cysteine residues in Keap1's BTB and IVR domains, resulting in a conformational change in Keap1. The low-affinity DLG motif separates from Keap1, while the high-affinity ETGE motif keeps binding to Keap1. The Keap1-cul3 complex loses ubiquitin ligase activity to Nrf2. Nrf2 accumulates in the cytoplasm and metastasizes to the nucleus, upregulating transcription of downstream genes.
