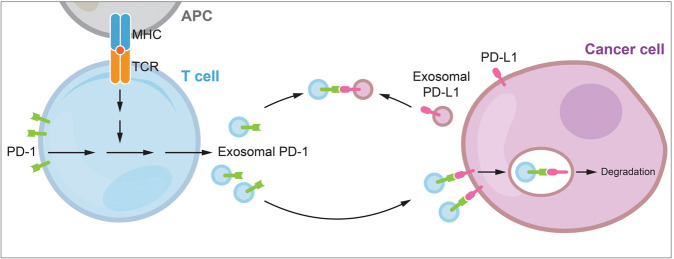
Fig. 7. A proposed model of PD-L1 blockade by activated T cell-derived exosomal PD-1 particles.
T cells activated upon antigen recognition release exosomal PD-1 to restrict surface and exosomal PD-L1-induced inhibition. Exosomal PD-1 can either block surface PD-L1 loci and induce consequent tumor PD-L1 internalization via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, or neutralize exosomal PD-L1 and prevent its binding to T cell surface PD-1. Altogether, exosomal PD-1 helps to maintain T cell cytotoxicity against tumor cells.