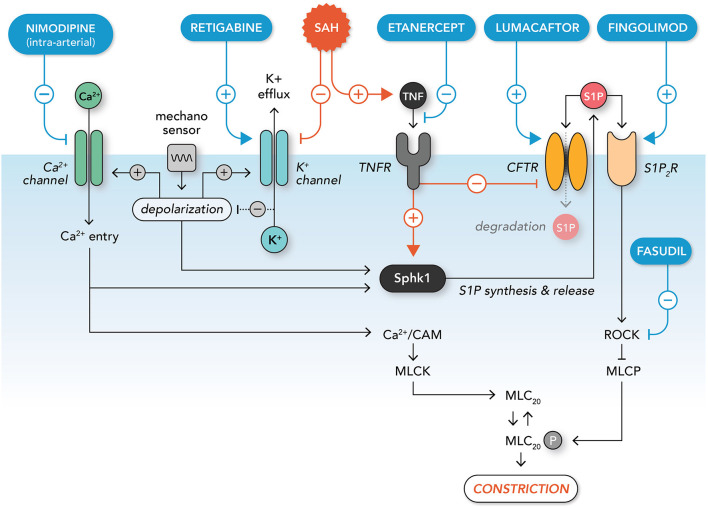
Figure 3.
Molecular mechanisms augmenting microvascular constriction in subarachnoid hemorrhage and potential interventions. A mechanosensitive complex initiates myogenic vasoconstriction via membrane potential depolarization: this leads to calcium entry via opening of voltage-gated calcium channels; voltage gated potassium channels also open, leading to hyperpolarizing potassium efflux that limits the extent of depolarization (negative feedback). Intracellular calcium activates calmodulin (CAM), myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and the contraction apparatus. In addition, calcium entry and depolarization lead to the activation of sphingosine kinase 1 (Sphk1), which synthesizes and releases sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) into the extracellular compartment. Extracellular S1P activates the S1P2 receptor subtype (S1P2R), thereby activating the Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) signaling pathway. ROCK signaling inhibits myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP), which enhances MLCK's activation of the contractile apparatus. Extracellular S1P is sequestered from S1P2R by the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), which transports S1P across the plasma membrane for degradation. In subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), potassium channels are down-regulated, leading to enhanced depolarization through disinhibition. SAH also stimulates inflammatory tumor necrosis factor signaling, which down-regulates CFTR expression and enhances the activation of Sphk1. This increases pro-constrictive S1P / S1P2R / ROCK signaling, which enhances constriction via the inhibition of MLCP. Therapeutics targeting these pathological processes include: (i) intra-arterially-delivered nimodipine (calcium channel blocker; limits calcium entry), (ii) retigabine (potassium channel activator; reduces depolarization), (iii) etanercept (inhibits TNF signaling; reduces S1P synthesis and increases S1P degradation), (iv) lumacaftor (increases CFTR expression; increases S1P degradation), (v) fingolimod (stimulates S1P receptor internalization; inhibits ROCK activation), and (vi) fasudil (ROCK inhibitor; limits inhibition of MLCP).