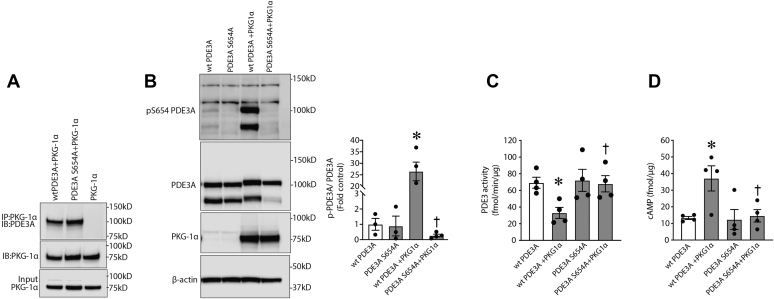
Figure 6.
PKG-Iα–dependent phosphorylation of PDE3A at S654inhibits PDE3A activity and protects intracellular cAMP from degradation.A, in HEK293T cells, overexpressed PKG-Iα associates with both wtPDE3A and mutant S654A-PDE3A. B, however, only wtPDE3A is phosphorylated at S654 when cells were treated with 8-bromo-cGMP (4 h). C, the activity of wtPDE3A was also downregulated by PKG-Iα overexpression, whereas the S654A-mutant PDE3A was unaffected. D, similarly, cAMP levels were increased by PKG-Iα overexpression in cells expressing wtPDE3A but not in cells expressing the S654A-PDE3A mutant. Data in B represent mean ± SEM, n = 3. ∗p < 0.05 wtPDE3A alone versus wtPDE3A + PKG-Iα; †p < 0.05 mutPDE3A + PKG-Iα versus wtPDE3A + PKG-Iα. Data in C and D represent mean ± SEM, n = 4. ∗p < 0.05 wtPDE3A alone versus wtPDE3A + PKG-Iα; †p < 0.05 wtPDE3A + PKG-Iα versus mutPDE3A + PKG-Iα. HEK293T, human embryonic kidney 293T cells; PDE3A, phosphodiesterase 3A; PKG-Iα, protein kinase G-Iα; S654, serine 654.