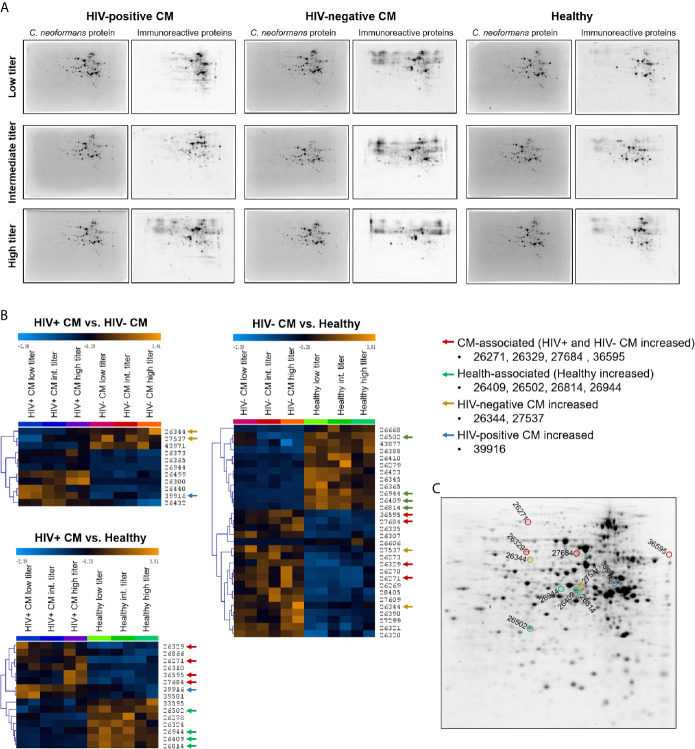
Figure 3.
Two-dimensional (2D) analysis of the immunoproteome recognized by cryptococcal meningitis (CM) patients and healthy individuals revealed infection- and health-associated spots. Cryptococcus neoformans proteins (strain H99) were separated by 2D gel electrophoresis and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes. (A) Representative blot images of total cryptococcal proteins (stained with UV-activated 2,2,2-trichloroethanol (TCE)) and immunoreactive protein spots bound by serum IgG (detected using AF-647 labeled secondary antibody) are shown. The contrast and brightness of the images were adjusted for publication and do not reflect actual signal intensities. (B) Heat maps of immunoreactive protein spots’ fluorescence signals recognized with different intensities by sera from different groups (p < 0.01). Spots were either (i) CM-associated (red arrows) – significantly stronger reactivity with CM patient sera (HIV-positive and HIV-negative) compared to healthy individuals, (ii) health-associated (green arrows) – significantly stronger reactivity with sera from healthy individuals compared to CM patients (HIV-positive and HIV-negative). Three spots were found that showed higher reactivity of (iii) HIV-negative sera (yellow arrows) or (iv) HIV-positive sera (blue arrows) compared to the respective other two groups. Immunoreactivity per sub-pool was determined in duplicates. Spot identifiers (row numbers) were automatically created by Delta 2D software. Analysis parameters: Test design: between-subjects, used Welch approximation, alpha: 0.01, p-values based on permutation, all permutations used: true, number of permutations per spot: 924, significance determined by standard Bonferroni correction, HCL: complete linkage, Euclidean Distance. (C) Spots of interest were highlighted in a 2D gel image. Proteins were stained with UV-activated TCE. Int., Intermediate.