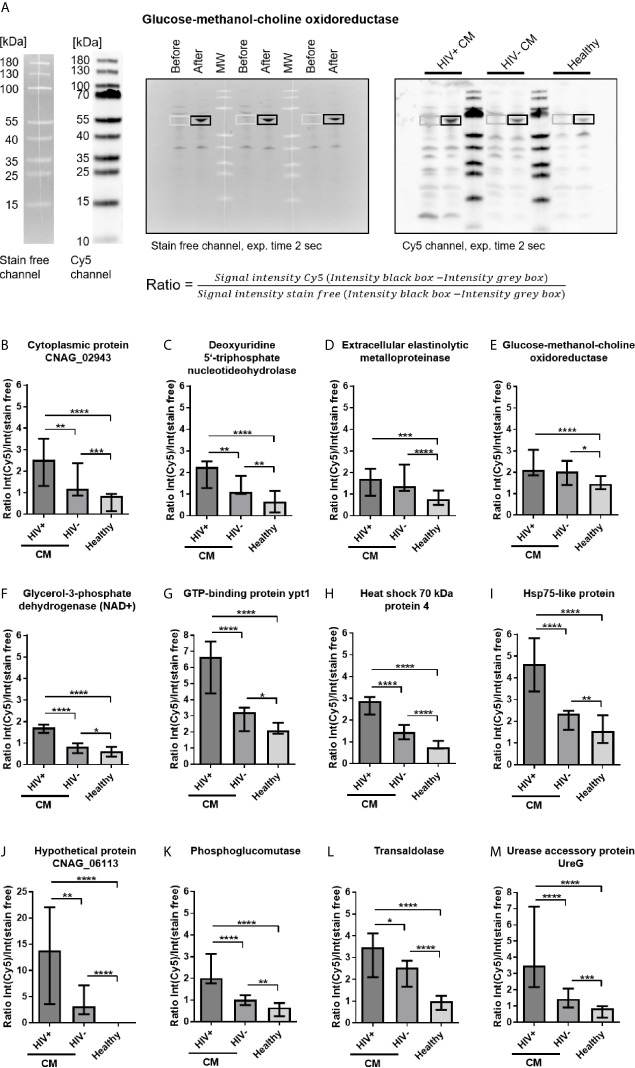
Figure 4.
Cryptococcal meningits (CM)-associated recombinant cryptococcal proteins reactive with serum IgG. (A) Escherichia coli lysates containing recombinant cryptococcal proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE. Samples before induction of recombinant protein expression and samples after induction of protein expression using IPTG were loaded, separated by MW markers, as representatively shown for glucose-methanol-choline oxidoreductase. E. coli proteins were blotted onto nitrocellulose membranes and (left) stained with 2,2,2-trichloroethanol (TCE, detection in stain free channel). Membranes were incubated with pooled sera from HIV-positive (HIV+) CM patients, HIV-negative (HIV-) CM patients, or healthy control persons, as marked in the blot. (Right) Proteins immunoreactive with human IgG were detected using polyclonal goat-anti human IgG coupled to Alexa Fluor 647 (AF-647, detected in Cy5 channel). Ratios of fluorescence intensities of the respective area in both channels were calculated to normalize the immunosignal (Cy5 channel) onto the amount of protein loaded (stain free channel). (B–M) CM-associated cryptococcal proteins reactive with serum IgG are shown. Proteins depicted showed significantly stronger reactivity with sera from CM patients (HIV+ and HIV-) compared to sera from healthy individuals. Median values and range of three independent experiments, comprising values from three different exposure times for each experiment, are shown. Statistical analysis was carried out using the Mann–Whitney U test for comparison of two groups. Asterisks indicate significant difference. MW, Molecular weight marker; exp., exposure.