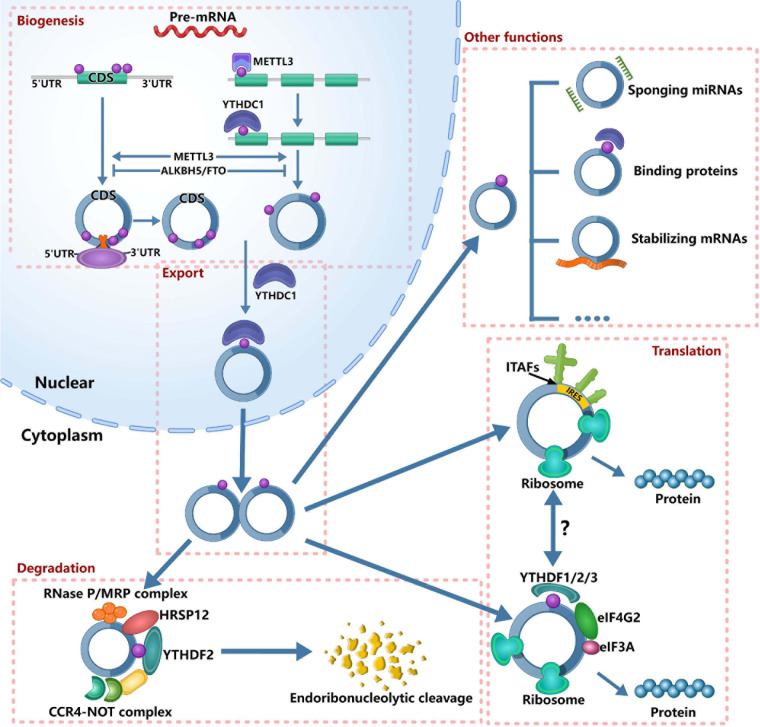
FIGURE 1.
Roles of m6A in circRNA metabolism. It’s has confirmed that m6A can regulate circRNA metabolism, including circRNAs biogenesis, translation, degradation and cellular localization. On the one hand, m6A sites located around the start and stop codons in linear mRNAs can recruit spliceosome, leading to back splicing and circRNA production. On the other hand, m6A deposition and YTHDC1 binding to exons can regulate circularization. In the nucleus, the m6A can bind specific nuclear reader proteins, mainly YTHDC1, which can promote the export of circRNAs. Upon circRNAs export to the cytoplasm, m6A binds to specific reader proteins and other proteins to stabilize some mRNAs. The nuclear export of circRNAs also affects its miRNA sponges. The translation of circRNAs is only in cap-independent translation initiation mechanisms: IRES-dependent initiation of translation and m6A-dependent initiation of translation. m6A-driven translation of circRNA requires eIF4G2 and YTHDF3 and is enhanced by METTL3/14, inhibited by FTO. IRES-driven translation and m6A-driven translation may have interplays. Finally, m6A-modified circRNAs are endoribonuclease-cleaved via the YTHDF2-HRSP12-RNase P/MRP axis.