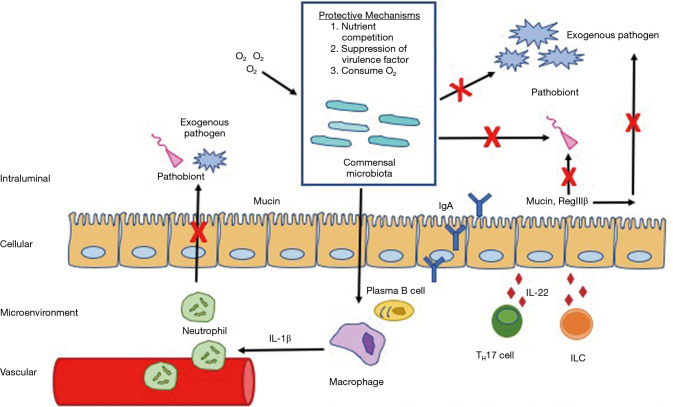
Figure 2.
Commensal microbiota inhibit colonization of exogenous pathogens and pathobionts through upregulation of host-immunity mediated resistance such as activating plasma B cells, macrophages, T-helper cells, and innate lymphoid cells. Commensal microbiota also competitively inhibit pathogens and pathobionts by uptake of nutrients, suppressing virulence factors, and consuming O2 needed for pathogen and pathobiont survival.