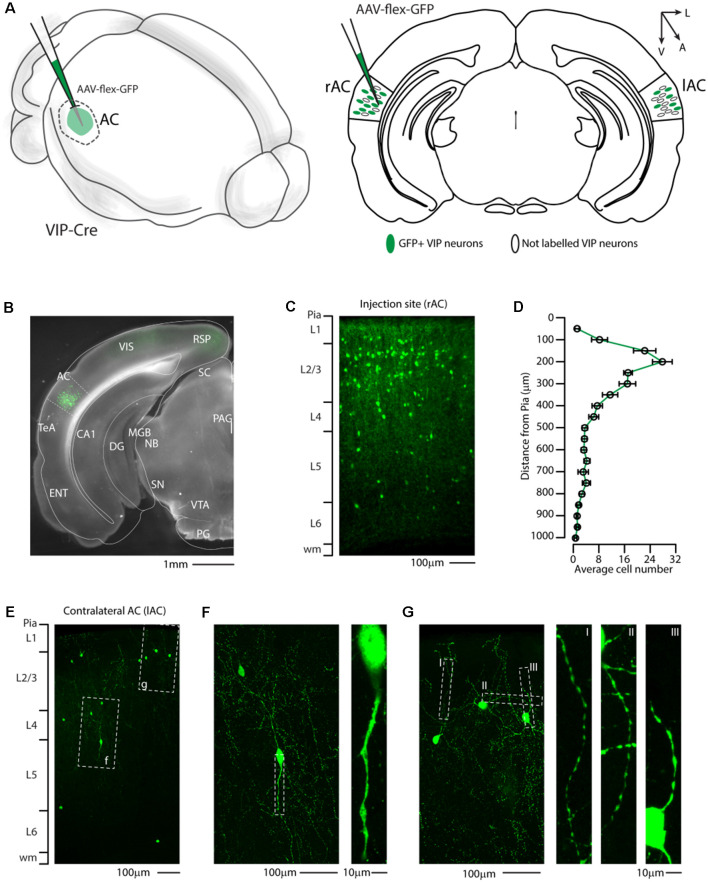
Figure 1.
Distribution of VIP-expressing neurons in the auditory cortex. (A) Schematic representation of right auditory cortex viral injection of AAV-flex-GFP. VIP-expressing neurons in both the injected (right AC, rAC) and contralateral (left, lAC) auditory cortex express GFP in a Cre-dependent manner. (B) Representative coronal section of an acute slice of the injection site (200 μm thick), with bright field (gray) and GFP expressing neurons (green). The Allen brain atlas coronal table superimposed for reference indicates the correct targeting of the auditory cortex. Scale bar: 1 mm. (C) High magnification confocal image of the injection site showing GFP expressing neurons in the right auditory cortex. Scale bars: 100 μm. (D) Laminar distribution of VIP neurons in the auditory cortex, quantified every 50 μm from Pia (0) to white matter (1 mm). Data are expressed ad mean ± s.e.m. (E) Representative high magnification confocal image of the contralateral Auditory cortex showing retrograde labeled GFP expressing neurons. Scale bars: 100 μm. (F,G) Details of dashed square (f and g) of (E), with corresponding high magnification of the dendritic arborization of GFP+ VIP-expressing neurons showing their characteristic thin and aspiny morphology. Scale bars: 100 μm and 10 μm. RSP, retrosplenial cortex; VIS, visual cortex; TeA, temporal association cortex; AC, auditory cortex; ENT, enthorinal cortex; CA1, Cornu Ammonis of the hippocampus subfield 1; DG, dentate gyrus; SC, superior colliculus; MGB, medial geniculate body; NB, nucleus of the brachium of the inferior colliculus; PAG, periacqueductal gray; SN, substantia nigra; VTA, ventrotegmental area; PG, pontine gray.