Table 1.
Effect of natural compounds on the modulation of autophagy in stroke or other neurological disorders.
| Natural compound | Autophagy regulation | Potential implication | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
Urolithin A 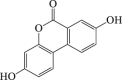
|
Autophagy flux↑LC3-II ↑ SQSTM1 ↓ |
Parkinson's disease94 Cerebral stroke96 |
93, 94, 95, 96 |
Tomatidine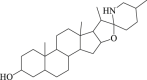
|
Autophagy flux↑ Lysosomal activation ↑ |
Alzheimer's disease97 Cerebral stroke100 |
97, 98, 99, 100 |
Spermidine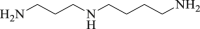
|
Autophagy flux ↑ Beclin 1 ↑ SQSTM1 ↓ |
Cerebral stroke103,104 | 101, 102, 103, 104 |
Anthocyanidin 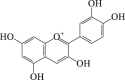
|
LC3-II ↑ ROS ↓ |
Cerebral stroke105 | 105 |
Astragaloside IV 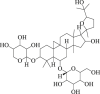
|
LC3-II ↑ SQSTM1 ↓ |
Parkinson's disease106 Depression107 Cerebral ischemia108 |
106, 107, 108 |
Curcumin 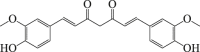
|
Autophagy flux ↓ LC3-II ↓ SQSTM1 ↑ |
Cerebral stroke111,112 | 109, 110, 111, 112 |
Schizandrin A 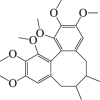
|
Beclin 1↓ LC3-II ↓ mTORC 1 ↑ AMPK↓ | Cerebral stroke113, 114, 115 | 113, 114, 115 |
Ascorbic acid 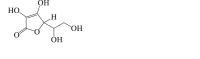
|
Beclin 1↓ LC3-II ↓ |
Neurotoxicity116 Seizure117 |
116,117 |
Ginkgolic acid 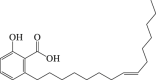
|
mTORC 1 ↓ LC3-II ↑ Beclin 1 ↑ ATG-5 ↑ |
Parkinson's disease120 | 118, 119, 120 |
α-Arbutin 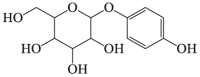
|
ROS ↓ AMPK-p62 autophagy pathway |
Parkinson's disease122,123 | 121, 122, 123 |
Glycyrrhizic acid 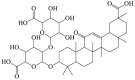
|
LC3-II ↑ Beclin 1 ↑ |
Parkinson's disease125,126 | 124, 125, 126 |
Euxanthone 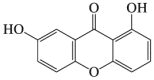
|
LC3-II ↑ Beclin 1 ↑ SQSTM1 ↓ |
Neurite outgrowth126 Alzheimer's disease129 |
127, 128, 129 |
Morroniside  Loganin 
|
LC3-II ↑ Beclin-1 ↑ ATG7 ↑ ATG12 ↑ |
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion130 Traumatic brain injury131 Alzheimer's disease132 |
130, 131, 132 |
Resveratrol 
|
LC3-II ↑ ATG 4 ↑ SQSTM1 ↓ |
Spinal cord injury133 Alzheimer's disease134 Huntington's disease135,136 |
133, 134, 135, 136 |
Genistein 
|
LC3-II ↑ TFEB ↑ |
Alzheimer's disease139 Parkinson's disease140 Huntington's disease141 |
137, 138, 139, 140, 141 |
Trehalose 
|
TFEB ↑ LC3-II ↑ |
Parkinson's disease143 Alzheimer's disease144 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis145 |
142, 143, 144, 145 |
p-Coumaric acid 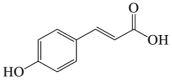
|
LC3-II ↑ SQSTM1 ↓ |
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis148 | 146, 147, 148 |
Diallyl trisulfide 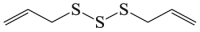
|
LC3-II ↑ ROS ↓ |
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis150,151 | 149, 150, 151 |
