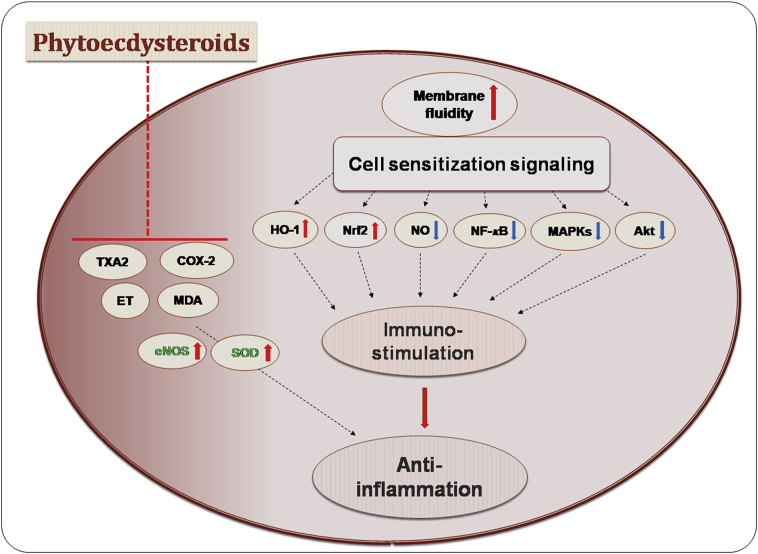
Figure 10.
Overview of anti-inflammatory effects of phytoecdysteroids. Phytoecdysteroids tend to interfere with the membrane fluidity which leads to cell sensitization and modulate various cellular signaling processes in immunomodulation and inflammation. This especially involves the inhibition of NF-κB, COX-2, MDA, MAPKs and Akt, and activation of HO-1, Nrf2, eNOS and SOD. Akt, protein kinase B; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ET, endothelin; HO-1, hemaoxygenase-1; MAPKs, mitogen-activated protein kinases; MDA, malondialdehyde; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; NO, nitric oxide; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TXA2, thromboxane A2.