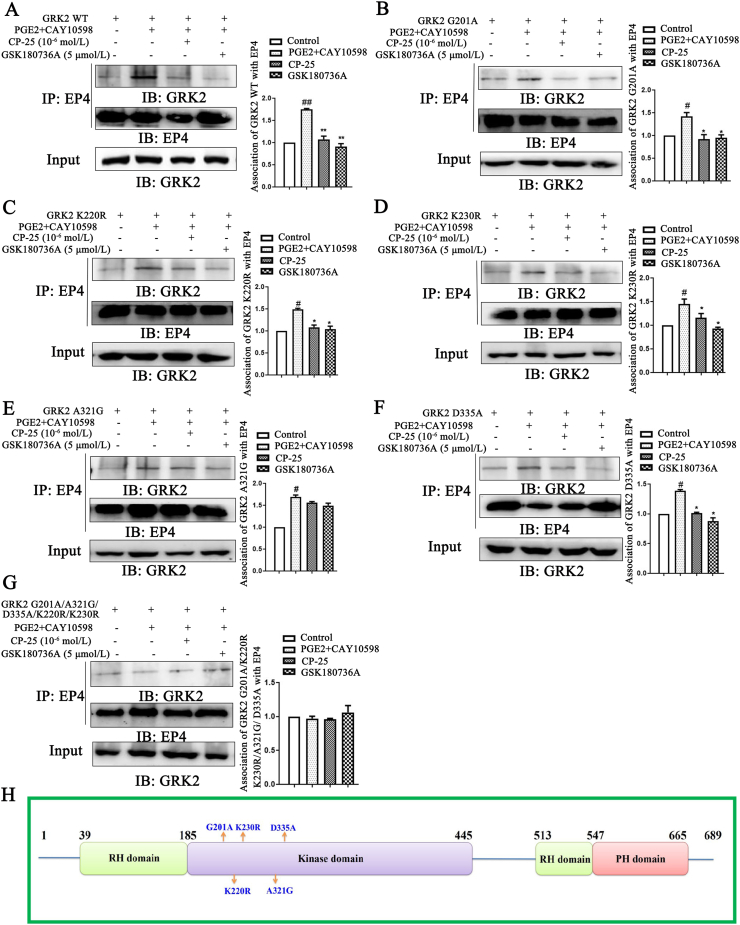
Figure 7.
Study on the binding sites of CP-25 and GRK2. HEK 293T cells transfection with pIRES-EGFP-GRK2 WT (A), pIRES-EGFP-GRK2 G201A (B), pIRES-EGFP-GRK2 K220R (C), pIRES-EGFP-GRK2 K230R (D), pIRES-EGFP-GRK2 A321G (E), pIRES-EGFP-GRK2 D335A (F), and pIRES-EGFP-GRK2 G201A/K220R/K230R/A321G/D335A (G) plasmids were challenged with CAY10598 (1 μmol/L) following a 1 h pre-treatment with PGE2 (10 μmol/L) for 30 min in the presence and absence of CP-25 (10−6 mol/L) or GSK180736A (5 μmol/L). The association of GRK2 mutants and EP4 was determined by co-IP using the EP4-specific antibody and subsequent blotting with GRK2-specific (n = 3). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. control group; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 vs. PGE2+CAY10598 group. (H) Location of mutations made in the GRK2 domain. Light green bars represent the regulator of G-protein signaling (RGS) homology (RH) domain, light purple bars represent kinase domain and pink bars represent Pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. G201, K220, K230, A321, and D335 residues are those that were mutated in this study.