Figure 2.
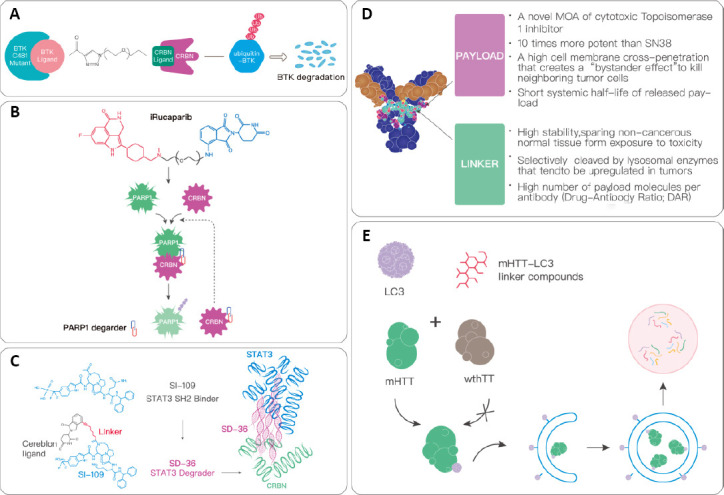
The applications of PROTACs.
(A) CRBN protein is recruited to the BTK protein with a C481S mutation by the BTK protein lysator. This causes the proteins to be ubiquitinated, after which they are recognized and degraded by proteasomes. (B) iRucaparib-AP6 is a PARP1 degrading agent, and is directly connected to the binding molecule of CRBN at the end of rucaparib through a PEG6 linker. PARP1 is finally recognized and degraded by the ubiquitin-protease system. (C) SD-36 is a STAT3 degrading agent. It is composed of a linker that connects the STAT3 SH2 binder (S1–109) and CRBN. It can degrade STAT3 via a proteasome with a ubiquitin tag. (D) Compared with ordinary chemotherapeutics, ADC has seven main advantages. (E) Small molecule drugs degrade mHTT through the autophagy pathway. During autophagy, the key protein LC3 is polymerized and diffused after lipolysis to form the membrane structure, and the degradation targets such as proteins, lipids, and organelles are encapsulated in it to form a complete autophagosome. This is fused with lysosomes and the encapsulated substance is degraded. ADC: Antibody-drug conjugate; BTK: Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; CRBN: cereblon ligand; LC3: microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3; mHTT: mutant huntingtin; MOA: mechanisms of action; PEG6: polyethylene glycol 6; PROTACs: proteolysis-targeting chimeric molecules; STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; wthTT: wild type huntingtin protein.
