Figure 1.
Experimental protocol, structure of luteolin, and dose-dependent tests.
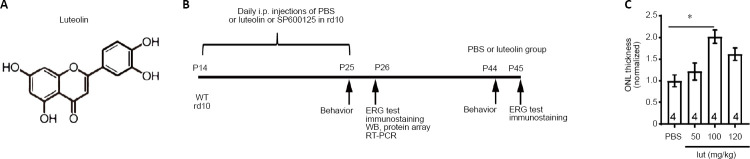
(A) Chemical structure of luteolin. (B) Experimental protocol. In the first set of experiments, rd10 mice at P14 were daily i.p. injected with PBS (n = 28) or luteolin (n = 30) until P25, when assessments started. Age-matched WT mice (n = 25) were utilized as normal controls. Another 13 rd10 mice were kept until P45 to test the long-term effect of luteolin. In the second set of experiments, PBS (n = 4), luteolin (n = 4), or the c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor SP600124 (n = 4) was injected into rd10 mice from P14 to P25. (C) Dose-dependent effects of luteolin (lut) on ONL thickness in rd10 mice at 1 mm away from the center of the optic disk. Values were normalized to PBS-treated controls. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test). Numbers within bars indicate quantities of mice tested. ERG: Electroretinogram; i.p.: intraperitoneal; ONL: outer nuclear layer; P: postnatal day; PBS: phosphate-buffered saline; RT-PCR: real-time polymerase chain reaction; WB: western blot; WT: wild-type.