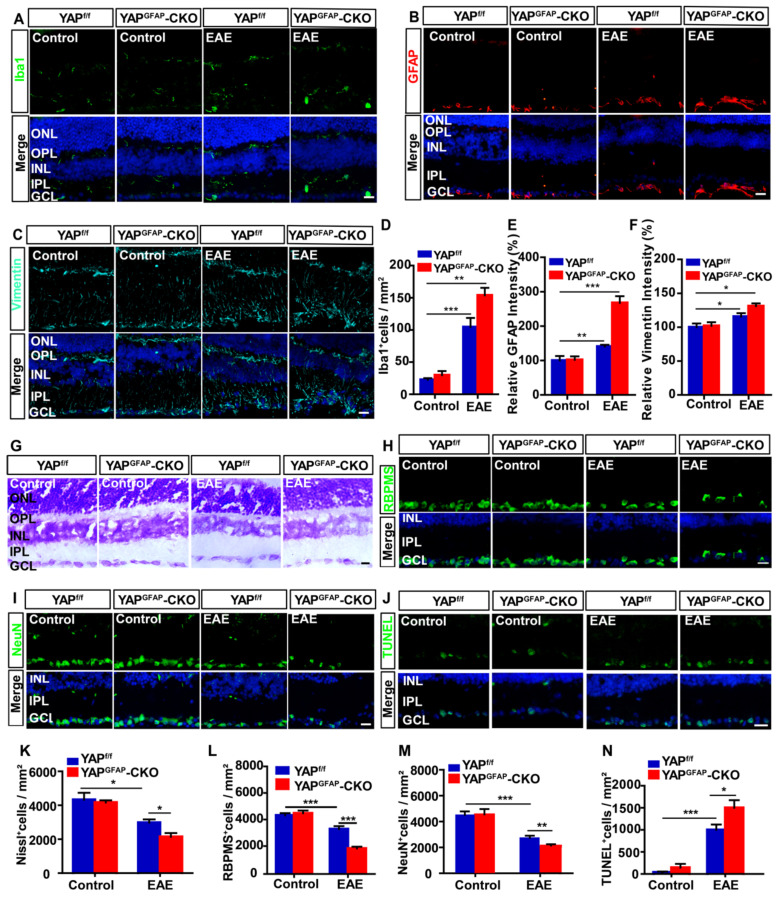
Figure 5.
Ablation of YAP in astrocytes exacerbates the inflammation and induces the apoptosis in retina of EAE mice. (A-C) Immunostaining of Iba1 (green) (A), GFAP (red) (B) or Vimentin (cyan) (C) in the retina of YAPf/f and YAPGFAP-CKO mice, YAPf/f EAE and YAPGFAP-CKO EAE mice. (D) Quantitative analysis of the density of Iba1+ cells as shown in (A) (n = 7 per group). (E-F) Quantitative analysis of the relative GFAP intensity (E) or Vimentin intensity (F) as shown in (B-C) (n = 8 per group, normalized to control). (G) Representative images of Nissl staining in the retina of YAPf/f and YAPGFAP-CKO mice, YAPf/f EAE and YAPGFAP-CKO EAE mice. (H-I) Immunostaining of RBPMS (green) (H) or NeuN (green) (I) in the retina of YAPf/f and YAPGFAP-CKO mice, YAPf/f EAE and YAPGFAP-CKO EAE mice. (J) Immunostaining analysis of cell apoptosis by TUNEL staining in the retina of YAPf/f and YAPGFAP-CKO mice, YAPf/f EAE and YAPGFAP-CKO EAE mice. (K) Quantitative analysis of the density of Nissl+ cells as shown in (G) (n = 11 per group). (L-M) Quantitative analysis of the density of RBPMS+ cells (L) or NeuN+ cells (M) as shown in (H-I) (n = 7 per group). (N) Quantitative analysis of the density of TUNEL+ cells as shown in (J) (n = 9 per group). Data were mean ± SEM, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post-tests, compared with YAPf/f group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Scale bars, 20 μm.