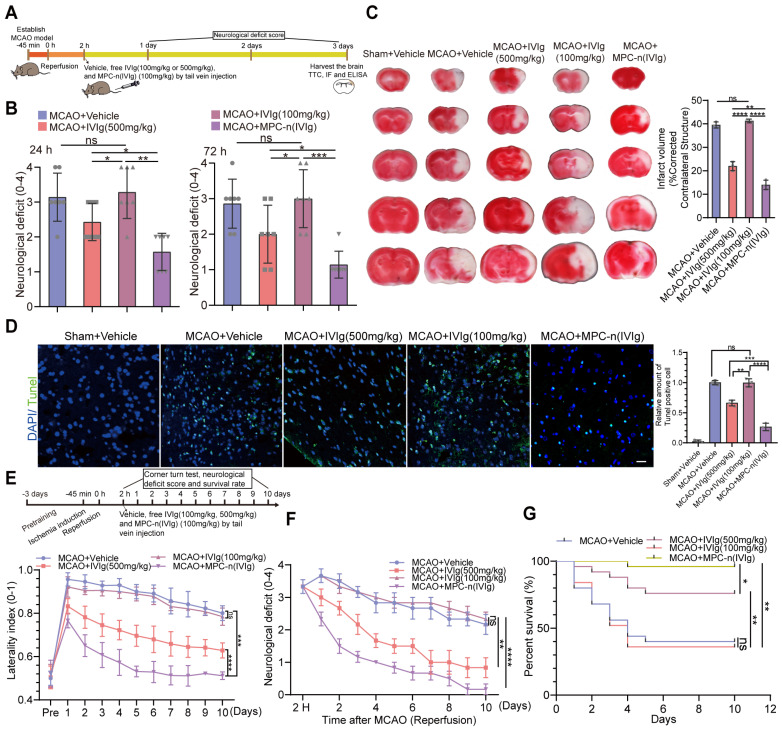
Figure 5.
Therapeutic efficacy of MPC-n(IVIg) in MCAO mice. A) The experimental protocol used. B) Neurological deficit scores 24 or 72 h post-injection of vehicle (same volume), free IVIg (500 and 100 mg/kg), or MPC-n(IVIg) (100 mg/kg) 2 h post-ischemic-reperfusion in mice (n = 7). C) Representative images of TTC staining in the brain sections 3 d post-injection. The infarction area is indicated in the white color. The infarct volume was measured in the whole hemisphere and corrected by the contralateral structure (n = 3). MPC-n(IVIg) (100 mg/kg) was associated with a significant reduction in the infarct volume in the whole hemisphere compared to the vehicle and free IVIg (500 and 100 mg/kg) controls. D) Fluorescence of TUNEL staining in the ischemic penumbra 3 d post-injection of vehicle (same volume), free IVIg (500 and 100 mg/kg), or MPC-n(IVIg) (100 mg/kg) 2 h post-ischemic-reperfusion in mice. In TUNEL staining, normal and apoptotic cell nuclei stained blue and green, respectively. TUNEL (green), and DAPI (blue). The histogram quantifies the TUNEL assay (n = 3). Scale bar = 20 μm. E) The corner turn test was analyzed using the laterality index (number of right turns-number of left turns)/10 (n = 10). F) Daily neurological deficit score was collected over the 10 recovery days. Group 1: MCAO mice injected with vehicle (n = 5); group 2: MCAO mice injected with IVIg (500 mg/kg; n = 5); group 3: MCAO mice injected with IVIg (100 mg/kg; n = 5), or group 4: MCAO mice injected with MPC-n(IVIg) (100 mg/kg; n = 5) for 10 d after injection. G) Mouse survival rates 10 d post-injection of MPC-n(IVIg) (100 mg/kg) in the MCAO models (n = 25). Two hours after ischemic-reperfusion, the mice were administrated with vehicle, free IVIg (500 and 100 mg/kg), or MPC-n(IVIg) (100 mg/kg). All experiments were repeated independently three times. All data are presented as the mean ± S.D. ns, nonsignificant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, or ***P < 0.001.