Figure 3. Endogenous Dsx is essential for females to interpret the virgin behavioral state.
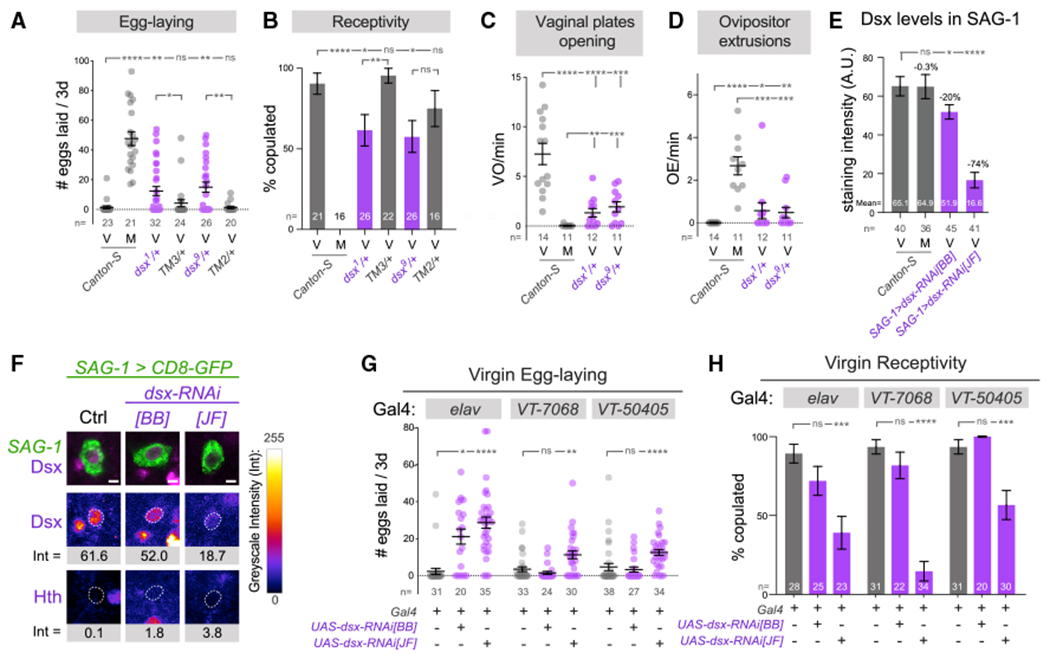
(A–D) Comparison of female behaviors in wild-type virgins, mated females, and doublesex heterozygotes, illustrating a partial transition to the mated state in the latter.
(E) Analysis of Dsx levels in abdominal SAG-1 neurons pre- and 24 h post-insemination and in virgins using independent dsx-RNAi transgenes. dsx-RNAi[JF] has a stronger effect on Dsx in SAG-1 neurons.
(F) Representative GFP-labeled abdominal SAG-1 neurons from average Dsx levels are shown, with corresponding Dsx and Hth staining. The dotted line corresponds to the nucleus of each neuron.
(G and H) Pan-neuronal knockdown of dsx results in increased egg-laying and decreased receptivity by female virgins. Restricted knockdown using VT-switch lines and dsx-RNAi[JF] transgene also induces virgin egg-laying and reduces receptivity.
Mann-Whitney non-parametric test (A, C–E, and G); Fisher’s exact test (B and H). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant. Error bars, SEM. Scale bar, 2 μm (F). Eggs were collected over 3 days for all virgin genotypes and over the first 24 h after copulation in mated flies (A and G). M, mated females; V, virgin females.
