Figure 8.
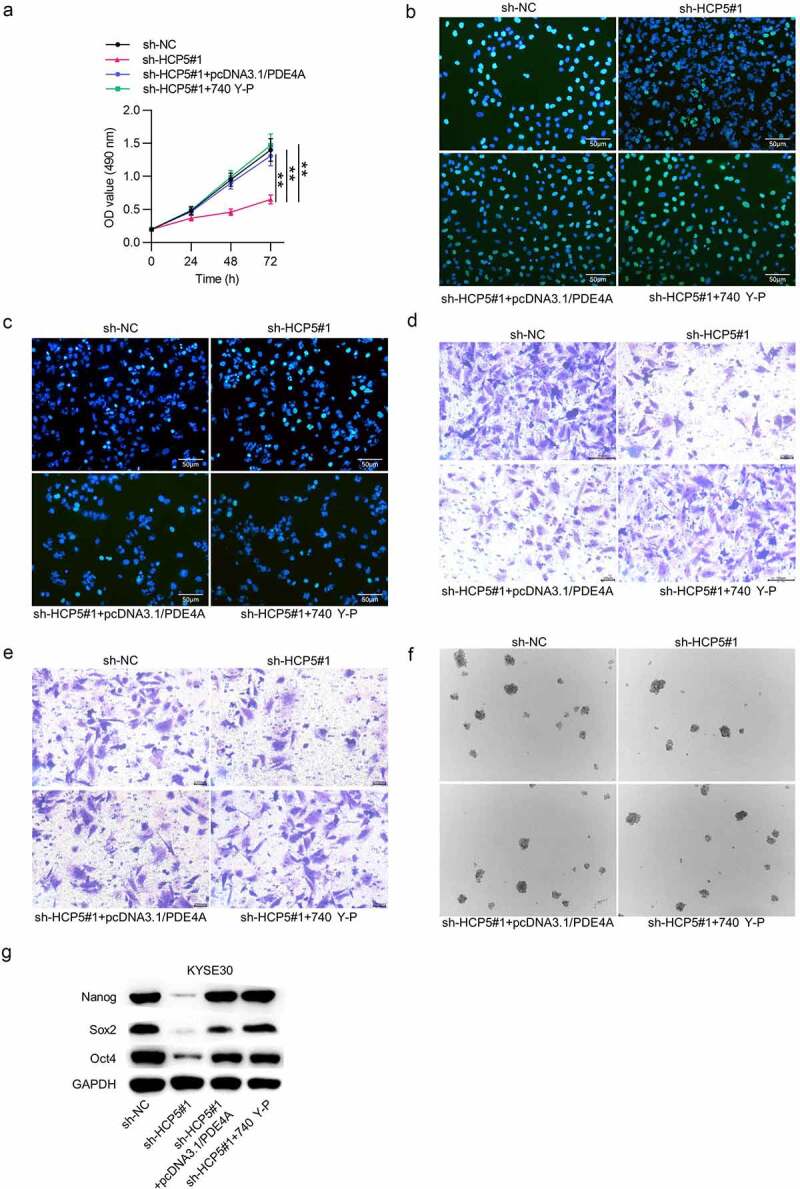
HCP5 facilitates ESCC cell malignant behaviors via the miR-139-5p/PDE4A and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways
(a–c) MTT and EdU assays were employed to detect KYSE30 cell viability and proliferation under different treatments: i. sh-NC, ii. sh-HCP5#1, iii. sh-HCP5#1+ pcDNA3.1/PDE4A, iv. sh-HCP5#1 + 740 Y-P. (d) TUNEL assay was adopted to assess KYSE30 cell apoptosis in each group: i. sh-NC, ii. sh-HCP5#1, iii. sh-HCP5#1+ pcDNA3.1/PDE4A, iv. sh-HCP5#1 + 740 Y-P. (e,f) The migrative and invasive abilities of KYSE30 cells under different treatments: i. sh-NC, ii. sh-HCP5#1, iii. sh-HCP5#1+ pcDNA3.1/PDE4A, iv. sh-HCP5#1 + 740 Y-P were examined with Transwell assays. (g) KYSE30 cell stemness characteristics in each group: i. sh-NC, ii. sh-HCP5#1, iii. sh-HCP5#1+ pcDNA3.1/PDE4A, iv. sh-HCP5#1 + 740 Y-P were accessed by sphere formation assay. (h) The expression levels of stemness-related proteins (Nanog, Sox2 and Oct4) in KYSE30 cells under different treatments: i. sh-NC, ii. sh-HCP5#1, iii. sh-HCP5#1+ pcDNA3.1/PDE4A, iv. sh-HCP5#1 + 740 Y-P were evaluated by western blot. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
