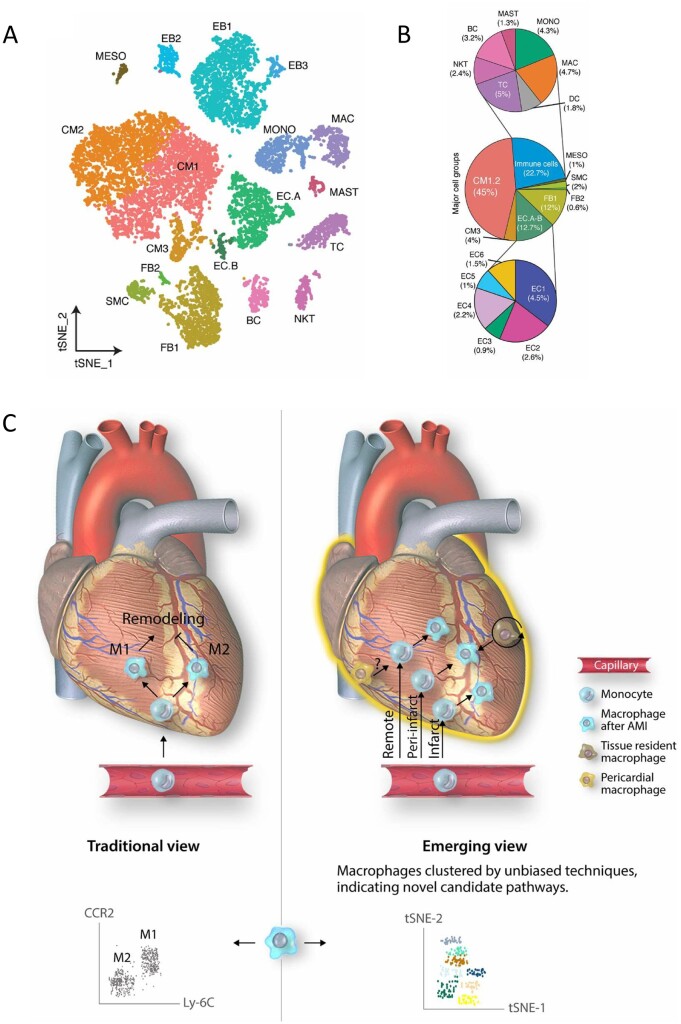
Figure 3.
(A) Identification of cell types in human foetal heart. Clustering for 12 461 cells from three healthy samples based on established lineage markers and visualized using t-SNE. (B) Averaged proportion of all cell types (except EBs) contributing to foetal human hearts. Middle panel indicates major cell groups with subgroups of immune cells (top panel) and endothelial cells (bottom panel) and number in parenthesis indicates percentage contribution to foetal heart cells. Figure taken from Suryawanshi et al.33 with permission. (C) Novel macrophage populations appear to play spatially restricted roles in remodelling of the myocardium following acute myocardial injury (AMI). Novel high throughput techniques allow unbiased resolution of cells into distinct populations, based on gene expression profile (scRNA-seq) or large panels of differentially expressed proteins (mass cytometry). Figure taken from Peet et al.34 with permission.