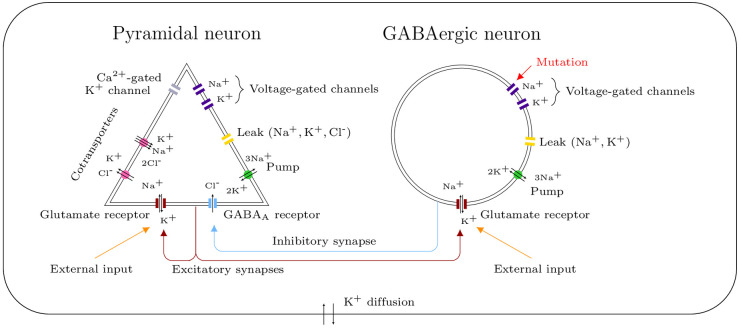
Fig 1. Schematic representation of the model.
Consider a pair of interconnected neurons in a closed volume. We modeled a GABAergic synapse from the GABAergic neuron to the pyramidal one, a glutamatergic synapse from the pyramidal neuron to the GABAergic one and a glutamatergic autapse from the pyramidal neuron to itself. The ion transport mechanisms represented here generate transmembrane ionic currents, which modify the membrane potentials of the neurons and the ion concentrations in the different compartments. The diffusion of extracellular potassium takes into account both passive diffusion and glial buffering. We modeled external stimuli, which reflect the activity of the surrounding network or mimic experimental depolarizations, with glutamate inputs on the glutamatergic receptors. The implementation of NaV1.1’s genetic mutations affects only the GABAergic neuron.