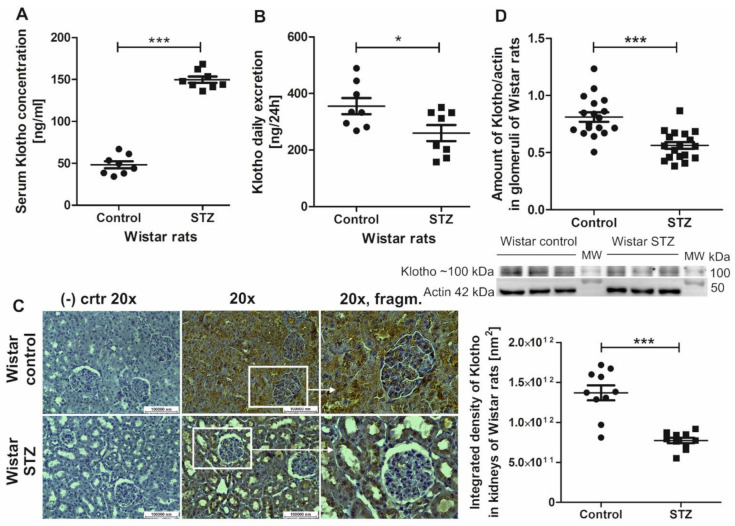
Figure 1.
Klotho protein levels increase in serum in Wistar rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes (STZ) and decrease in their whole kidney tissue, glomeruli, and urine. (A) Despite the elevation of Klotho protein levels in serum in STZ rats (*** p < 0.0001, vs. control, unpaired t-test, n = 8), (B) a significant decrease in 24-h urinary Klotho excretion was found in STZ rats (* p = 0.03, vs. control, unpaired t-test, n = 8). This may have resulted from (C) a significant decrease in Klotho protein levels (renal tissue staining in brown) in glomeruli and cells that form tubules of nephrons in the kidneys in STZ rats (*** p < 0.0001, vs. control, unpaired t-test, n = 10). This was also concordant with (D) the downregulation of Klotho protein expression in glomeruli in STZ rats (*** p < 0.0001, vs. control, unpaired t-test, n = 18). (−) ctrl, negative control; MW, molecular weight.