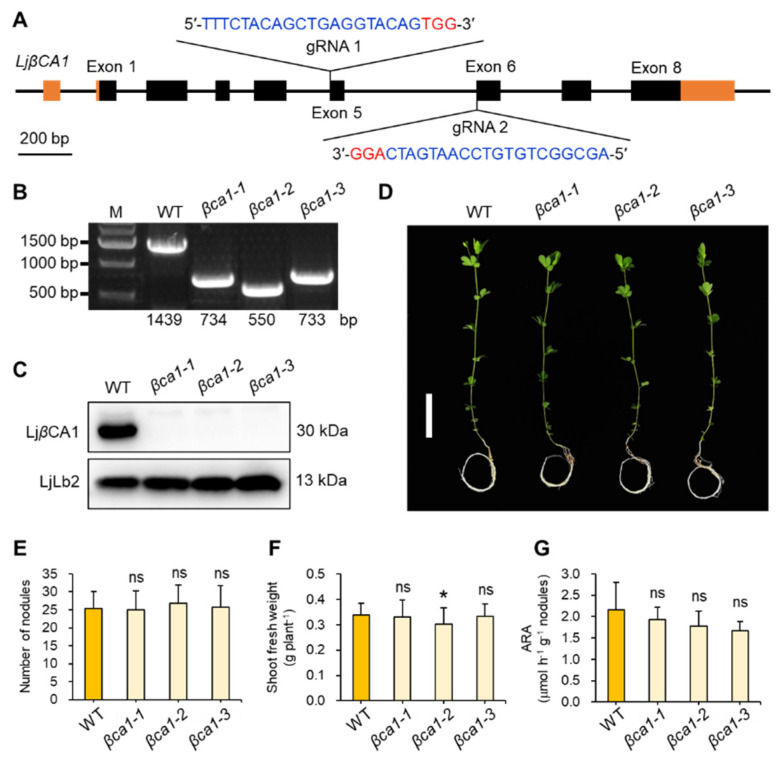
Figure 5.
Construction and symbiotic phenotype analyses of LjβCA1 mutants. (A) Gene structure and gRNA design of LjβCA1. Black boxes indicate the exons and orange boxes indicate the 5′ or 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs). Two gRNAs used for the LjβCA1 knockout experiment were located in exon 5 and exon 6, respectively. The PAM sequence is marked in red. The 20 bp gRNA sequence is marked in blue. (B) Genotyping information of three LjβCA1 mutants, including βca1-1, βca1-2, and βca1-3. (C) Western blot analysis of three LjβCA1 mutants using LjβCA1 and LjLb2 antibody. (D) The symbiotic phenotype of LjβCA1 mutants at 5 wpi. Plants were grown in nitrogen-deficient conditions after inoculation with M. loti MAFF303099. Three CRISPR/Cas9-derived independent LjβCA1 mutant lines (βca1-1, βca1-2, and βca1-3) were compared to the WT plants. Scale bar, 5 cm. SNF parameters include (E) root nodule number, (F) shoot fresh weight, and (G) ARA per nodule fresh weight of WT and mutant plants. Values are means ± SD of 30 plants per genotype. Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis in (E–G) by comparing respective mutant lines to WT plants. ns, not significant; *, p < 0.05. Phenotyping analysis has been performed three times, and similar results were obtained.