Fig. 1. Midbrain DA neurons require PINK1 to survive when fission is compromised.
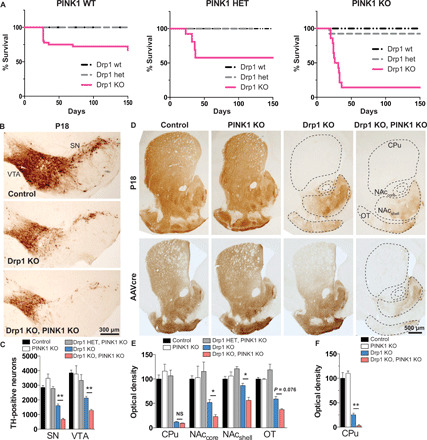
(A) Kaplan-Meier survival curve of Drp1 wt, heterozygous (het), and Drp1KO mice on a PINK1 wt background (left), PINK1 het background (middle), and PINK1 KO background (right). Drp1KO-PINK1KO mice were significantly more likely to die than either Drp1KO-PINK1 wt [hazard ratio (HR) 14.4, 95% confidence interval (CI): 4.67 to 44.6, P < 0.001 by log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test] or Drp1KO-PINK1 het mice (HR 4.21, 95% CI: 1.50 to 11.8, P < 0.01). n = 18 to 36 PINK1 wt mice per group, 5 to 13 PINK1 het mice per group, and 13 to 15 PINK1 KO mice per group. Data in left (PINK1 WT) were published (2) and reproduced here with permission from The Journal of Neuroscience. (B and C) Targeted deletion of Drp1 in DA neurons causes loss of DA cell bodies in the SN and VTA by P18 (assessed by TH staining), which is exacerbated by concurrent PINK1 loss. Data show means ± SEM, n = 4 mice per group with 5 to 6 fields per mouse. In (D) (top) and (E), the loss of cell bodies is preceded by early loss of DA terminals projecting to the caudate putamen (CPu) by P18. Although DA projections to the nucleus accumbens (NAc) core and shell and to the olfactory tubercule (OT) are relatively spared in Drp1KO, concurrent loss of PINK1 markedly increases their susceptibility. n = 4 mice per group, 14 to 20 fields per mouse. In (D) (bottom) and (F), AAVcre was delivered to the SNc of 6- to 7-month-old Drp1lox/lox and Drp1lox/lox;PINK1KO mice. Two months later, mice lacking PINK1 were more susceptible to Drp1 loss, indicating that the synergistic effect also occurs in adult animals. n = 3 to 5 mice per group with 4 to 5 fields per mouse. NS, not significant; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 by one-way ANOVA with Games-Howell post hoc test.
