Figure 6.
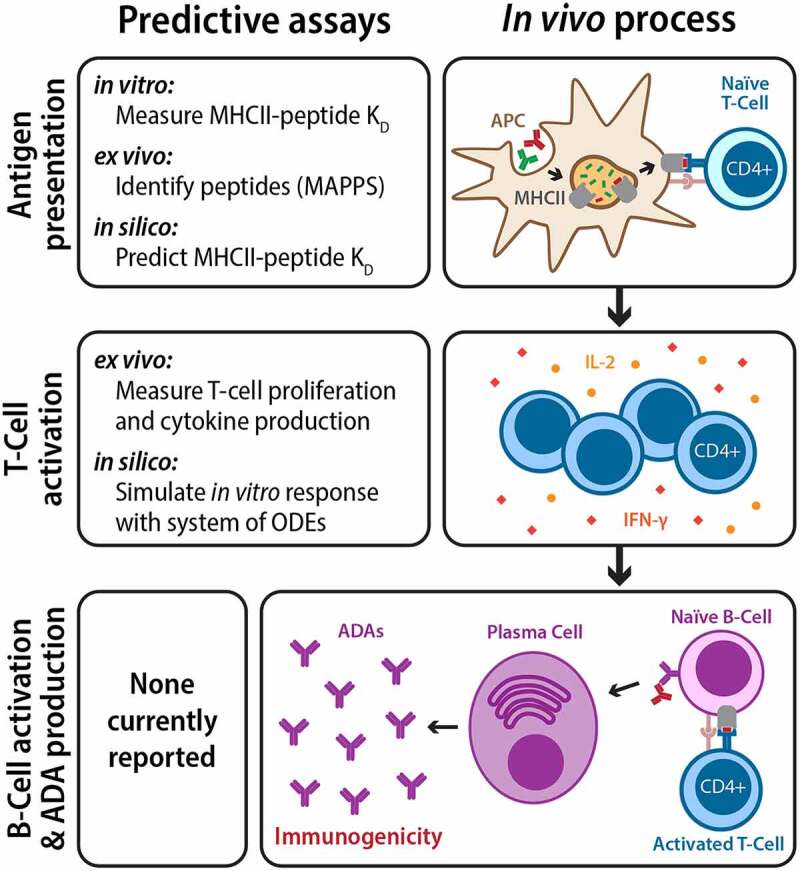
Repeated administration of therapeutic antibodies can lead to the development of anti-drug antibodies and immunogenicity. Antibody therapeutics are first internalized by APCs and processed into peptides, some of which are presented by the major histocompatibility complex II (MHCII) as foreign antigens to naïve T cells (top). Activated T cells then proliferate, release chemokines, and activate naïve B-cells (middle). Activated B-cells mature into plasma cells and produce ADAs in large quantities, leading to immunogenicity (bottom). While there are currently no reported assays for directly predicting clinical immunogenicity, various steps in the ADA development process can be modeled and predicted
