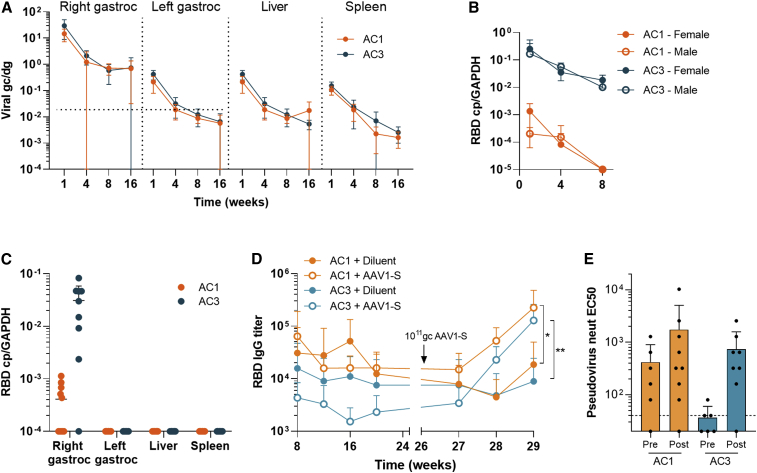
Figure 5.
Pharmacology of AAVCOVID vaccines in mice
(A) Quantification of vector genome copies (DNA, genome copies/diploid genome or gc/dg) in the right gastrocnemius (right gastroc) or injection site, left gastrocnemius (left gastroc) or contralateral muscle, liver, and spleen on weeks 1, 4, 8, and 16 after the administration of 1011 gc of AC1 or AC3 in C57BL/6 animals (n ≥ 6, 3–5/gender). Horizontal dotted lines indicate background levels for right and left gastrocnemius muscles. Liver and spleen had not detectable background.
(B) Quantification of transgene expression (RBD copies/GAPD copies or RBD cp/GAPDH) in the right gastrocnemius muscle.
(C) Quantification of expression (RBD copies/GAPD copies or RBD cp/GAPDH) in the injection site (right gastroc), contralateral muscle (left gastroc), liver and spleen on week 16.
(D and E) SARS-CoV-2 RBD-binding antibody titer 29-week follow-up in BALB/c mice (n ≥ 9) vaccinated with 1010 gc of AC1 and AC3 on week 0 and revaccinated with 1011gc of AAV1-S (open circles) or diluent (solid circles) on week 26.
(E) Pseudovirus neutralizing titers in animals described in (D) before and after the boost with AAV1-S.
(A–E) Data are represented as mean ± SD. (D and E) Student’s t test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.