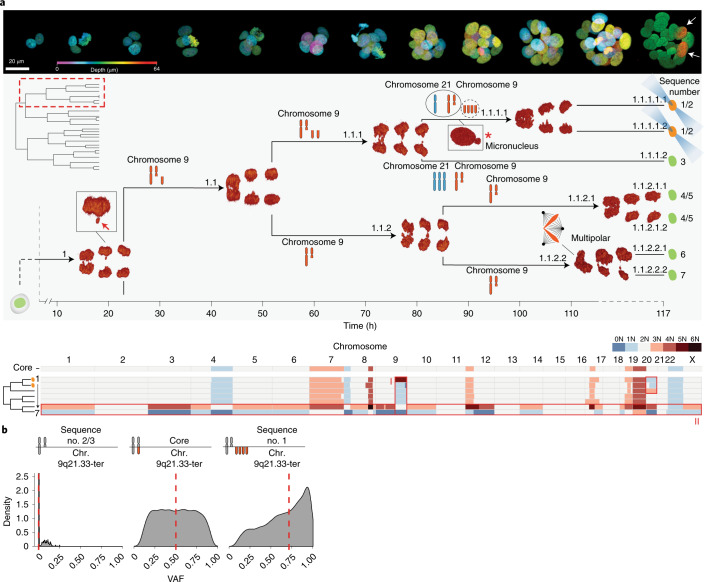
Fig. 3. Acentric chromosomal fragments are prone to cycles of replication and collective missegregation.
a, 3D Live-Seq dataset of a PDTO-9 organoid consisting of 25 cells (100% recovery). Top: representative stills of the growing PDTO-9 structure with nuclei coded in false color by depth. The final still shows two photoconverted cells (white arrows) that were the progeny of branch 1.1 of the mitotic tree. Branch 1.1 is highlighted (dashed red box) in the full tree structure in the top left of the middle panel and enlarged as the main image in the middle panel, with 3D-rendered stills of each anaphase. The onset of anaphase is indicated by arrowheads in relation to the time axis. Bottom: karyotype heatmap of all cells mapped to branch 1.1 (cells 1–7) and a reference core karyotype of the imaged PDTO. The sequence numbers of the mapped sequencing results in relation to the mitotic tree are indicated, including the photoconversion state of each cell. Chromosome cartoons along enlarged branch 1.1 indicate reconstructed copy-number changes across cell generations. The inset of cell division 1 shows a lagging chromatin structure, as indicated by the red arrow. The asterisk highlights the presence of a micronucleus in cell 1.1.1.1 that persists until nuclear envelope breakdown. b, The variant allele frequency (VAF) distribution of variants located on the acentric chromosome 9q fragment (Chr. 9q21.33-ter) is consistent with two rounds of replication and collective missegregation for cell number 1. The VAF of SNVs located on the missegregated chromosome 9q21.33-ter region is 0% for cell numbers 2 and 3 (only one copy of chromosome 9q) and 50% for a cell with the core karyotype. Cell number 1 shows nearly 80% VAF for these SNVs, indicative that four of the five chromosome 9q21.33-ter copies originated from the same parental allele. The dashed red line indicates the median.