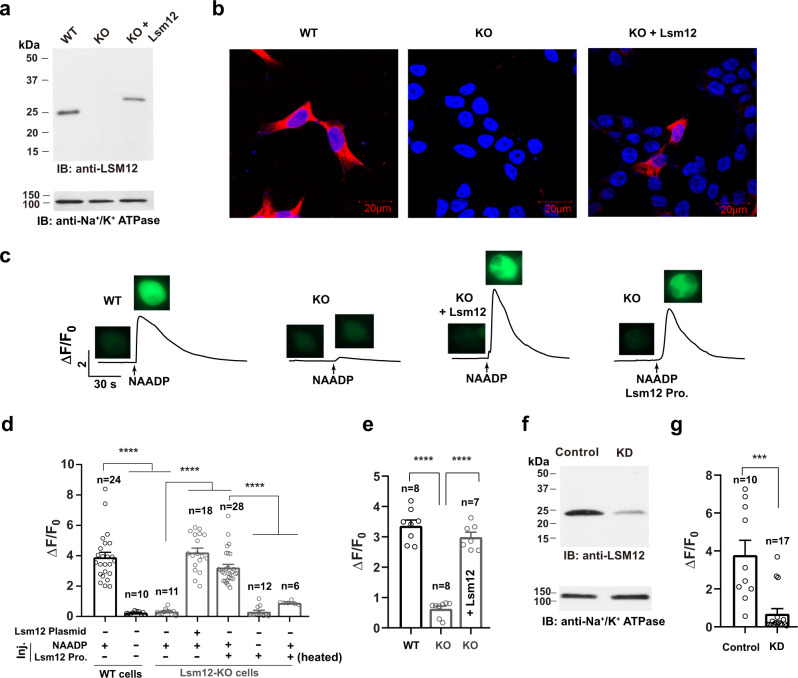
Fig. 2. Lsm12 is essential for NAADP-evoked Ca2+ release.
a, b Immunoblot (a) and immunofluorescence (b) assays show the loss of Lsm12 expression in the Lsm12-KO cell line. Lsm12 and cell nuclei are shown in red and blue, respectively. c Time course and cell images of NAADP-induced change in fluorescence of Ca2+ indicator in TPC2-expressing HEK293 WT and Lsm12-KO cells with/without exogenous Lsm12 expression or protein injection. Cell images were taken before NAADP injection and at the peak of Ca2+ increase after injection. d Averaged NAADP-induced changes in Ca2+ indicator fluorescence in TPC2-expressing HEK293 WT and Lsm12-KO cells. Exogenous Lsm12 was introduced to cells by either plasmid transfection or protein injection (labeled at the bottom). e Averaged NAADP-induced changes in Ca2+ indicator fluorescence in TPC1-expressing HEK293 WT and Lsm12-KO cells. Exogenous Lsm12 was introduced to cells by plasmid transfection (labeled in the column). f Immunoblot of Lsm12 in cell lysates of SK-BR-3 control and Lsm12-KD cells. g Averaged NAADP-induced changes in Ca2+ indicator fluorescence in TPC2-expressing SK-BR-3 control and Lsm12-KD cells. Data were presented as mean value ± SEM. Unpaired Student’s t-test (two-tailed) was used to calculate p values. *** and **** are for p values ≤ 0.001 and 0.0001, respectively. IB immunoblot, KO knockout, Pro. protein, Inj. injection, KD knockdown.